Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(n_{H^+}=n_{HCl}=0,5.0,3=0,15\left(mol\right)\\ n_{OH^-}=2.n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,2.a.2=0,4a\left(mol\right)\\ Vì:pH=1\Rightarrow-log\left[H^+\right]=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[H^+\right]=0,1\left(M\right)\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{n_{H^+\left(dư\right)}}{0,5}=0,1\\ \Rightarrow n_{H^+\left(dư\right)}=0,05\left(mol\right)\\ \Rightarrow0,15-0,4a=0,05\\ \Leftrightarrow a=0,25\)

Đáp án C
Sau phản ứng pH = 12 ⇒ O H - dư
[ O H − ] d u = 10 − 2 M
n O H − d u = 0 , 01.0 , 2 = 0 , 002 m o l
Phản ứng:
H + + O H − → H 2 O V ậ y n O H − b đ = 0 , 01 + 0 , 002 = 0 , 012 m o l O H − b đ = 0 , 012 / 0 , 1 = 0 , 12 M
C M ( N a O H ) = 0 , 02 M .

Đáp án D
Dd axit ban đầu có [H+] =0,1 M → nH+=0,1.0,1 =0,01 mol
Dd sau phản ứng có pH = 12 → dư bazo và có pOH =14-12=2 → [OH-] =0,01M→ nOH = 0,002 mol
PTHH: H+ + OH- → H2O
Ta có nNaOH = nH+ + nOH dư = 0,01 + 0,002 = 0,012 mol → a = 0,12M

Đáp án D
nH+ = 0,1.0,1= 0,01
Trong dụng dịch sau phản ứng có nOH- = 0,01 .0,2=0,002
⇒ nOH- ban đầu = n H+ + n OH-dư = 0,01+0,002=0,012
⇒ a = 0,012 ÷ 0,1 =0,12
Đáp án D.

Ta có
\(\text{nHCl=0,2.0,1=0,02(mol)}\)
\(\text{nH2SO4=0,2.0,05=0,01(mol)}\)
2HCl+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaCl2+2H2O
H2SO4+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaSO4+2H2O
Ta có pH=13\(\rightarrow\)Ba(OH)2 dư
pH=13\(\rightarrow\)pOH=1\(\Rightarrow\)CM[OH-]=0,1(M)
\(\rightarrow\)CMBa(OH)2 dư=0,05(M)
\(\text{nBa(OH)2 dư=0,05.0,5=0,025(mol)}\)
\(\text{m=0,01.233=2,33(g)}\)
nBa(OH)2=0,025+0,02/2+0,01=0,045(mol)
\(\rightarrow\)a=\(\frac{0,045}{0,3}\)=0,15(M)
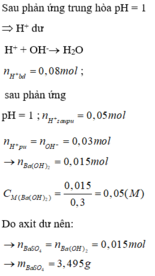

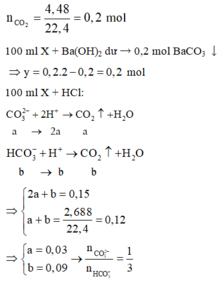
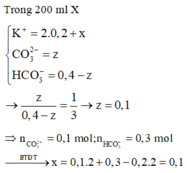
$n_{HCl} = 0,2.0,175 = 0,035(mol)$
$n_{HCl\ dư} = 0,5.10^{-pH} = 0,5.10^{-2} = 0,005(mol)$
$\Rightarrow n_{HCl\ pư} = 0,035 - 0,005 = 0,03(mol)$
$KOH + HCl \to KCl + H_2O$
$n_{KOH} = n_{HCl\ pư} = 0,03(mol)$
$a = 0,03 : 0,3 = 0,1M$