
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


5.
Tọa độ dỉnh của (P) là: \(I\left(-\dfrac{b}{2a};\dfrac{-\Delta}{4a}\right)\Rightarrow I\left(1;-4m-2\right)\)
Để I thuộc \(y=3x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow-4m-2=3.1-1\)
\(\Rightarrow m=-1\)
6.a.
Với \(a\ne0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}64a+8b+c=0\\-\dfrac{b}{2a}=5\\\dfrac{4ac-b^2}{4a}=12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}64a+8b+c=0\\b=-10a\\4ac-b^2=48a\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}c=-64a-8b=-64a-8\left(-10a\right)=16a\\b=-10a\\4ac-b^2=48a\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow4a.16a-\left(-10a\right)^2=48a\)
\(\Rightarrow a=-\dfrac{4}{3}\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{40}{3}\Rightarrow c=-\dfrac{64}{3}\)
Hay pt (P): \(y=-\dfrac{4}{3}x^2+\dfrac{40}{3}x-\dfrac{64}{3}\)
b.
Thay tọa độ 3 điểm vào pt (P) ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}c=-1\\a+b+c=-1\\a-b+c=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=-1\\c=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Pt (P): \(y=x^2-x-1\)
c.
Do (P) đi qua 3 điểm có tọa độ (1;16); (-1;0); (5;0) nên ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b+c=16\\a-b+c=0\\25a+5b+c=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-2\\b=8\\c=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay pt (P) có dạng: \(y=-2x^2+8x+10\)

\(A=\left(m-2;6\right),B=\left(-2;2m+2\right).\)
Để \(A,B\ne\varnothing\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m-2\ge-2\\2m+2>6\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m\ge0\\m>2\end{cases}}\)
Kết hợp ĐK \(2< m< 8\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left(2;8\right)\)

a ) \mathbb{R} \backslash (-3; \, 1]R\(−3;1]=(-∞;-3]∪(1;+∞)
b) (-\infty; \, 1) \backslash [-2; \, 0](−∞;1)\[−2;0]=(- (-\infty; \, 1) \backslash [-2; \, 0]∞;-2)∪(0;1)
a ) R\(−3;1]=(-∞;-3]∪(1;+∞)
b) [-2; \, 0](−∞;1)\[−2;0]= [-2; \, 0]∞;-2)∪(0;1)

✳️ Giải thích các điều kiện
📌 Điều kiện 1: \(A \subset \mathbb{R} \backslash B\)
- Tức là mọi phần tử của \(A\) không thuộc \(B\) → \(A \cap B = \emptyset\)
- Nghĩa là: Không có phần tử chung giữa \(A = \left(\right. - \infty ; m \left.\right)\) và \(B = \left[\right. 3 m + 1 ; 3 m + 2 \left]\right.\)
👉 Điều này xảy ra khi:
\(\left(\right. - \infty ; m \left.\right) \cap \left[\right. 3 m + 1 ; 3 m + 2 \left]\right. = \emptyset\)
→ Tức là:
\(m \leq 3 m + 1\)
Giải bất phương trình:
\(m \leq 3 m + 1 \Rightarrow - 2 m \leq 1 \Rightarrow m \geq - \frac{1}{2}\)
📌 Điều kiện 2: \(A \cap B \neq \emptyset\)
Tức là: phải có phần tử chung giữa \(A = \left(\right. - \infty ; m \left.\right)\) và \(B = \left[\right. 3 m + 1 ; 3 m + 2 \left]\right.\)
→ Tức là:
\(\left(\right. - \infty ; m \left.\right) \cap \left[\right. 3 m + 1 ; 3 m + 2 \left]\right. \neq \emptyset\)
→ Điều này xảy ra khi tồn tại \(x \in \left[\right. 3 m + 1 ; 3 m + 2 \left]\right.\) sao cho \(x < m\)
→ Nói cách khác:
\(3 m + 1 < m\)
Giải bất phương trình:
\(3 m + 1 < m \Rightarrow 2 m < - 1 \Rightarrow m < - \frac{1}{2}\)
✅ Kết luận
- Từ (1): \(m \geq - \frac{1}{2}\)
- Từ (2): \(m < - \frac{1}{2}\)
⛔ Hai điều kiện mâu thuẫn nhau → Không có giá trị \(m\) nào thỏa mãn đồng thời cả hai điều kiện.

a) \(B\subset A\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-4;5\right)\subset\left(2m-1;m+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2m-1\le-4< 5\le m+3\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2m-1\ge4\\5\le m+3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m< -\frac{3}{2}\\m\ge2\end{cases}}\left(ktm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\varnothing\)
b) \(A\text{∩ }B=\varnothing\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m+3< -4\\5< 2m-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m< -7\\m>3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(m< -7;m>3\)

8.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=a>0\\\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=x^2+1\)
Pt trở thành:
\(\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}+2a=3b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}=3b-2a\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=4a^2-12ab+9b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2-12ab+10b^2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\a=5b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\\\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=5\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+3=x^2+4x+5\\x^2+2x+3=25\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\24x^2+98x+122=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.
ĐKXĐ: \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{1-x}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2+2b^2=3-x=-\left(x-3\right)\)
Pt trở thành:
\(a-2b-3ab=-\left(a^2+2b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+a^2-3ab+2b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+\left(a-b\right)\left(a-2b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-b+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\a+1=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=2\sqrt{1-x}\\\sqrt{1+x}+1=\sqrt{1-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+x=4\left(1-x\right)\\x+2+2\sqrt{1+x}=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x=3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\-1-2x=2\sqrt{1+x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1-2x\ge0\\\left(-1-2x\right)^2=4\left(1+x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^2=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{\dfrac{3}{5};-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right\}\)

a) (-\infty ; \, 2) \cap (-1; \, +\infty)(−∞;2)∩(−1;+∞)=(-1;2)
b) (−1;6) ∪ [4;8)=(-1;8]
c) (−∞;−5] ∩(−5;1)={-5}a) (-\infty ; \, 2) \cap (-1; \, +\infty)(−∞;2)∩(−1;+∞)=(-1;2)
b) (−1;6) ∪ [4;8)=(-1;8]
c) (−∞;−5] ∩(−5;1)={-5}

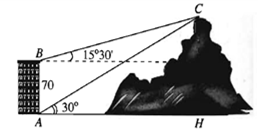
ˆABC=90°+15°30'=105°30'
Xét tam giác ABC có ˆCAB =60°, ˆABC=105°30' ta có:
ˆCAB+ˆABC+ˆACB=180° (định lí tổng ba góc trong tam giác)
⇒ˆACB=180°−ˆCAB−ˆABC
⇒ˆACB=180°−60°−
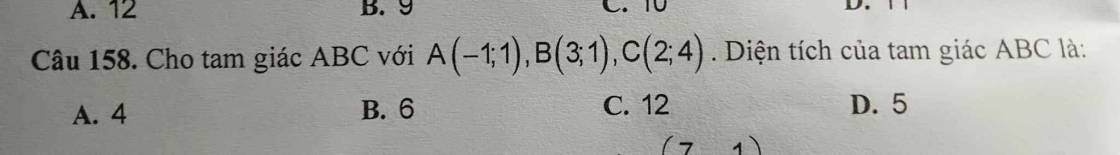
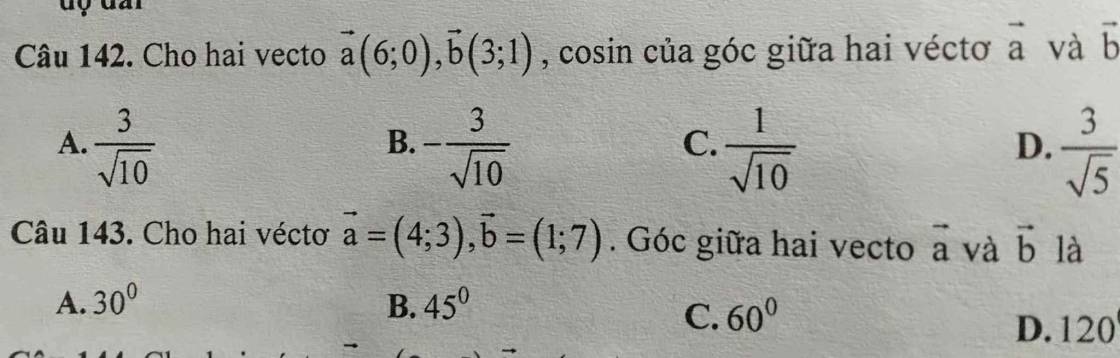


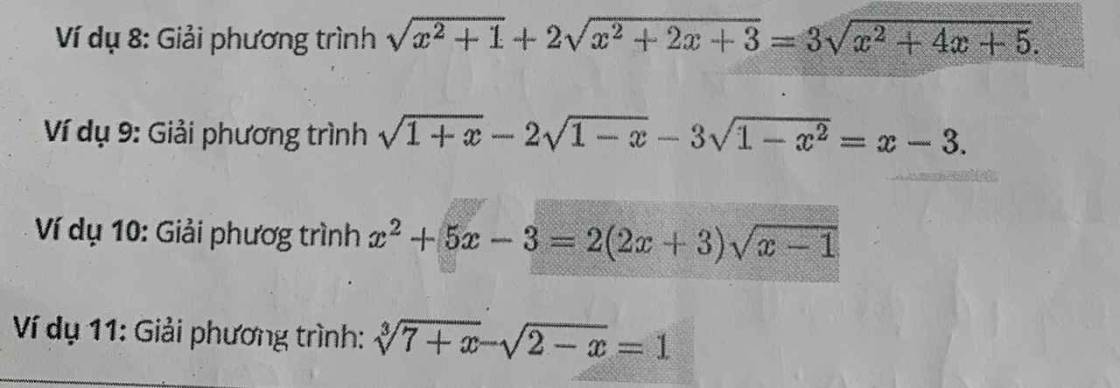

Câu 158:
A(-1;1); B(3;1); C(2;4)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(3+1\right)^2+\left(1-1\right)^2}=4\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(2+1\right)^2+\left(4-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{3^2+3^2}=3\sqrt{2}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(2-3\right)^2+\left(4-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{3^2+1^2}=\sqrt{10}\)
Xét ΔABC có \(cosBAC=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2-BC^2}{2\cdot AB\cdot AC}=\dfrac{16+18-10}{2\cdot4\cdot3\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
=>\(sinBAC=\sqrt{1-cos^2BAC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\cdot AC\cdot sinBAC\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot4\cdot3\sqrt{2}=6\)
=>Chọn B
Câu 143:
\(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(4;3\right);\overrightarrow{b}=\left(1;7\right)\)
\(\overrightarrow{a}\cdot\overrightarrow{b}=4\cdot1+3\cdot7=25\)
\(cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}\cdot\overrightarrow{b}}{\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|\cdot\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|}=\dfrac{25}{\sqrt{\left(4^2+3^2\right)}\cdot\sqrt{1^2+7^2}}=\dfrac{25}{5\cdot5\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)=>\(\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=45^0\)
=>Chọn B
Câu 142:
\(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(6;0\right);\overrightarrow{b}=\left(3;1\right)\)
\(cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}\cdot\overrightarrow{b}}{\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|\cdot\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|}=\dfrac{6\cdot3+1\cdot0}{\sqrt{6^2+0^2}\cdot\sqrt{3^2+1^2}}=\dfrac{18}{6\cdot\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}\)
=>Chọn A
Câu 131:
Đặt \(\overrightarrow{c}=x\cdot\overrightarrow{a}+y\cdot\overrightarrow{b}\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+\left(-4\right)y=-6\\3x+3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-12y=-18\\12x+12y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}18x=-14\\x+y=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{9}\\y=\dfrac{1}{3}-x=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{7}{9}=\dfrac{10}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Chọn A