
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

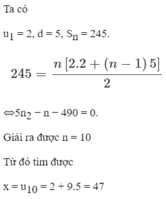

Bài làm
a)dãy số U: \(2,7,12,...x\)
U là cấp số cộng\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}d=u_2-u_1=7-2=5\\u_1=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(U_n=U_1+\left(n-1\right)d\)
=> \(n=\dfrac{U_n-U_1}{d}+1=\dfrac{x-2}{5}+1=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)}{5}\)
\(S_n=\dfrac{n\left(U_1+U_n\right)}{2}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)}{5}\left(2+x\right)}{2}=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}{2.5}=245\)
\(x^2+5x+6=2450\)
\(x^2+5x-2444=0\)
\(\Delta=5^2-4.\left(-2444\right)=9801=\)99^2
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-5-99}{2}< 0\left(loai\right)\\x_2=\dfrac{-5+99}{2}=47\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đáp số: x=47
b) Xét cấp số cộng 1, 6, 11, ..., 96. Ta có :
\(96=1+\left(n-1\right)5\Rightarrow n=20\)
Suy ra :
\(S_{20}=1+6+11+...+96=\dfrac{20\left(1+96\right)}{2}=970\)
và \(2x.20+970=1010\)
Từ đó : \(x=1\)

Giả sử 4 nghiệm phân biệt của phương trình là : \(x_1;x_2;x_3;x_4\)
Đặt \(x^2=y\ge0\), ta có phương trình :
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2-\left(3m+5\right)y+\left(m+1\right)^2=0\left(1\right)\)
Ta phải tìm m sao cho (1) có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(0 < y1 < y2\)
Khi đó (1) có 4 nghiệm là : \(x_1=-\sqrt{y_2};x_2=-\sqrt{y_1};x_3=-\sqrt{y_1};x_4=-\sqrt{y_2}\)
Rõ ràng \(x2 < x2 < x3 < x4\)
Theo đầu bài thì bốn nghiệm lập thành cấp số cộng, nên :
\(\Rightarrow x_3+x_1=2x_2\) V \(x_4+x_1=2x_3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{y_1}-\sqrt{y_2}=2\sqrt{y_1}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{y_1}=\sqrt{y_2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9y_1=y_2\) (*)
Áp dụng Viet cho phương trình (1) ta có hệ :
\(\begin{cases}\Delta=\left(3m+5\right)^2-4\left(m+1\right)^2>0\\S=y_1+y_2=10y_1=3m+5\\P=y_1y_2=9y_1^2=\left(m+1\right)^2\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}m=5\\m=-\frac{25}{19}\end{cases}\)

Vì 3 nghiệm phân biệt : \(x_1,x_2,x_3\) lập thàng cấp số cộng, nên ta có thể đặt :
\(x_1=x_0-d,x_2=x_0;x_3=x_0+d\left(d\ne0\right)\). Theo giả thiết ta có :
\(x^3+3x^2-\left(24+m\right)x-26-n=\left(x-x_1\right)\left(x-x_2\right)\left(x-x_3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-x_0+d\right)\left(x-x_0\right)\left(x-x_0-d\right)\)
\(=x^3-3x_0x^2+\left(3x^2_0-d^2\right)x-x^3_0+x_0d^2\) với mọi x
Đồng nhất hệ số ở hai vế của phương trình ta có hệ :
\(\begin{cases}-3x_0=3\\3x_0^2-d^2=-\left(24+m\right)\\-x_0^3+x_0d^2=-26-n\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x_0=-1\\3-d^2=-24-m\\1-d^2=-26-n\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x_0=-1\\m=n\end{cases}\)
Vậy với m = n thì 3 nghiệm phân biệt của phương trình lập thành cấp số cộng

\(f'\left(x\right)=1-\dfrac{2x}{\sqrt{x^2+12}}\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+12}\le2x\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+12\le4x^2\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^2\ge12\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2\ge4\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\ge2\)
Đáp số : \(\left[2,+\infty\right]\)

bài 1 bung công thức sin^6(x) + cos^6(x) là 5/8 + 3/8cos4x = cos4x chuyển vế giải
bài 2 dùng công thức hạ bậc sau đó dùng công thức cộng là ra