
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

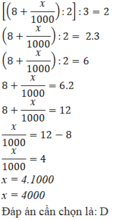

Bài 1 :
a) x < 0
b) x > 0
c) <=> 3 + |3x - 1| = 5
<=> |3x - 1| = 5 - 3 = 2
<=> 3x - 1 = 2 hoặc -3x + 1 = 2
<=> 3 x = 3 hoặc -3x = 1
<=> x = 1 hoặc x = -1/3
Bài 2 :
a) 27 = 33 < 3n < 243 = 35
<=> 3 < n < 5
Vì n thuộc N* nên n thuộc {4; 5}
b) 32 = 25 < 2n < 128 = 27
<=> 5 < n < 7. Vì n thuộc N* nên n = 6
c) 125 = 5 . 25 = 5 . 52 < 5.5n < 5 . 125 = 5 . 53
<=> 2 < n < 3. Vì n thuộc N* nên n = 3

Giải:
2\(^{x+1}\).3\(^{y}\) = 12\(^{x}\)
2.2\(^{x}\).3.3\(^{y-1}\) = 12\(^{x}\)
2.3.3\(^{y-1}\) = 12\(^{x}\): 2\(^{x}\)
6.3\(^{y-1}\) = 6\(^{x}\)
3\(^{y-1}\) = 6\(^{x}\): 6
3\(^{y-1}\) = 6\(^{x-1}\)
\(\begin{cases}y-1=0\\ x-1=0\end{cases}\)
\(\begin{cases}y=1\\ x=1\end{cases}\)
Vậy cặp số tự nhiên thỏa mãn đề bài là: (\(x;y\)) = (1; 1)

a)\(\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)^{2x+7}=\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)^4\)
=> 2x + 7 = 4
2x = 4 - 7
2x = -3
x = -3 : 2
x = -1,5
Vậy x = -1,5

a) \(\frac{x+7}{x+4}=\frac{2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(x+7\right)=2\left(x+4\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow5x+35-2x-8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=-27\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-9\)
b) \(\frac{2x-3}{2}=\frac{50}{2x-3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=100\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}2x-3=10\\2x-3=-10\end{array}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=\frac{13}{2}\\x=-\frac{7}{2}\end{array}\right.\)
c) \(\frac{x+1}{x-3}=\frac{x+3}{x+2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+2=x^2-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{11}{3}\)

\(TH1:a,2\left|x-3\right|+\left|2x+5\right|=11\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-6+2x+5=11\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-1=11\)
\(\Rightarrow4x=12\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(TH2:2\left|x-3\right|+\left|2x+5\right|=11\)
\(\Rightarrow-2x+6-2x-5=11\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x+1=11\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x=10\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-2,5\)
\(TH1:b,\left|x-3\right|+\left|5-x\right|+2\left|x-4\right|=2.2\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3+5-x+2x-8=4\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-6=4\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5\)
\(TH2:\left|x-3\right|+\left|5-x\right|+2\left|x-4\right|=4\)
\(\Rightarrow-x+3-5+x-2x+8=4\)
\(\Rightarrow-2x+6=4\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\)

a) Vì \(\left|1,4-x\right|\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left|1,4-x\right|\le0\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow-\left|1,4-x\right|-2\le-2\forall x\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow1,4-x=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=1,4\)
Vậy \(maxB=-2\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=1,4\)
b) \(D=\left|x-1\right|+\left|x-2\right|=\left|x-1\right|+\left|2-x\right|\)
\(\ge\left|x-1+2-x\right|=\left|1\right|=1\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\ge0\)
TH1: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\le0\\2-x\le0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\le1\\2\le x\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\le1\\x\ge2\end{cases}}\)( vô lý )
TH2: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\ge0\\2-x\ge0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge1\\2\ge x\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge1\\x\le2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow1\le x\le2\)
Vậy \(minD=1\)\(\Leftrightarrow1\le x\le2\)

Bài làm:
\(M=\left(12x^8+8x^2+6x-7\right)-\left(12x^8+2x-8\right)+\left(5-8x^2\right)\)
\(M=4x+6\)