
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1/ \(cosx=\frac{1}{3}\Rightarrow x=\pm a+k2\pi\) với \(cosa=\frac{1}{3}\)
Tổng các nghiệm:
\(\sum x=a+a+2\pi+\left(-a+2\pi\right)+\left(-a+4\pi\right)=8\pi\)
2/ ĐKXĐ:...
\(\Leftrightarrow1+tan^2x-2tanx-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^2x-2tanx-3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=-1\\tanx=3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=arctan3+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
b/ Không hiểu đề đoạn này \(sinx.cosx\left(x+\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\) , góc trong ngoặc không biết là của cái gì?
c/ ĐKXĐ:...
\(1+cot^2x+3tan^2x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{tan^2x}+3tan^2x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3tan^4x-4tan^2x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tan^2x=1\\tan^2x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=\pm1\\tanx=\pm\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=\pm\frac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
d/
ĐKXĐ: \(sinx\ne0\Rightarrow cosx\ne\pm1\)
\(2.cos^2x=1-cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos^2x+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-1\left(l\right)\\cosx=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx=cos\frac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x=-\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) cosx - √3sinx = √2 ⇔ cosx - tan![]() sinx = √2
sinx = √2
⇔ cos![]() cosx - sin
cosx - sin![]() sinx = √2cos
sinx = √2cos![]() ⇔ cos(x +
⇔ cos(x + ![]() ) =
) = ![]()
⇔ 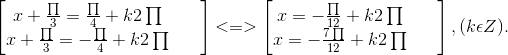
b) 3sin3x - 4cos3x = 5 ⇔ ![]() sin3x -
sin3x - ![]() cos3x = 1.
cos3x = 1.
Đặt α = arccos![]() thì phương trình trở thành
thì phương trình trở thành
cosαsin3x - sinαcos3x = 1 ⇔ sin(3x - α) = 1 ⇔ 3x - α = ![]() + k2π
+ k2π
⇔ x = ![]() , k ∈ Z (trong đó α = arccos
, k ∈ Z (trong đó α = arccos![]() ).
).

Bài 3. a) cos (x - 1) = ![]() ⇔ x - 1 = ±arccos
⇔ x - 1 = ±arccos![]() + k2π
+ k2π
⇔ x = 1 ±arccos![]() + k2π , (k ∈ Z).
+ k2π , (k ∈ Z).
b) cos 3x = cos 120 ⇔ 3x = ±120 + k3600 ⇔ x = ±40 + k1200 , (k ∈ Z).
c) Vì ![]() = cos
= cos![]() nên
nên ![]() ⇔ cos(
⇔ cos(![]() ) = cos
) = cos![]() ⇔
⇔ ![]() = ±
= ±![]() + k2π ⇔
+ k2π ⇔
.png)
d) Sử dụng công thức hạ bậc ![]() (suy ra trực tiếp từ công thức nhan đôi) ta có
(suy ra trực tiếp từ công thức nhan đôi) ta có
![]() ⇔
⇔ ![]() ⇔
⇔ ![]()
⇔ ![]() ⇔
⇔ ![]()

a/ Đề không rõ ràng bạn
Từ câu b trở đi, dễ dàng nhận ra tất cả các hàm số đều liên tục trên R
b/ Xét \(f\left(x\right)=x^3+3x^2-1\)
Ta có: \(f\left(-3\right)=-1\) ; \(f\left(-2\right)=3\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-3\right).f\left(-2\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(-3;-2\right)\)
\(f\left(0\right)=-1\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right).f\left(1\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(-2;0\right)\)
\(f\left(1\right)=3\Rightarrow f\left(0\right).f\left(1\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(0;1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có 3 nghiệm phân biệt
c/\(f\left(x\right)=m\left(x-1\right)^3\left(m^2-4\right)+x^4-3\)
\(f\left(-2\right)=13\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right).f\left(1\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(-2;1\right)\)
\(f\left(2\right)=13\Rightarrow f\left(1\right).f\left(2\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(1;2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 2 nghiệm
d/ \(f\left(x\right)=5sin3x+x-10\)
\(f\left(0\right)=-10\)
\(f\left(4\pi\right)=4\pi-10\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(0\right).f\left(4\pi\right)=-10\left(4\pi-10\right)< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc \(\left(0;4\pi\right)\) hay \(f\left(x\right)\) luôn có nghiệm

a.\(\frac{k\Pi}{2}+\frac{\alpha}{2}\)
b.\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{1}{4}arcsin\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)+\frac{k\Pi}{2}-\frac{1}{8}\\x=\Pi-\frac{1}{4}arcsin\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)+\frac{k\Pi}{2}-\frac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)