
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(9x^2-6x+3\)
\(=\left(9x^2-6x+1\right)+2\)
\(=\left(3x-1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
b: \(6x-x^2+1\)
\(=-\left(x^2-6x-1\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-6x+9-10\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-3\right)^2+10\le10\)

Đặt tính \(2n^2-n+2\) : \(2n+1\) sẽ bằng n - 1 dư 3
Để chia hết thì 3 phải chia hết cho 2n + 1 hay 2n + 1 là ước của 3
Ư(3) = {\(\pm\) 3; \(\pm\) 1}
\(2n+1=1\Leftrightarrow2n=0\Leftrightarrow n=0\)
\(2n+1=-1\Leftrightarrow2n=-2\Leftrightarrow n=-1\)
\(2n+1=3\Leftrightarrow2n=2\Leftrightarrow n=1\)
\(2n+1=-3\Leftrightarrow2n=-4\Leftrightarrow n=-2\)
Vậy \(n=\left\{0;-2;\pm1\right\}\)

Bài 1:
Vận tốc cano khi dòng nước lặng là: $25-2=23$ (km/h)
Bài 2:
Đổi 1 giờ 48 phút = 1,8 giờ
Độ dài quãng đường AB: $1,8\times 25=45$ (km)
Vận tốc ngược dòng là: $25-2,5-2,5=20$ (km/h)
Cano ngược dòng từ B về A hết:
$45:20=2,25$ giờ = 2 giờ 15 phút.

Bài 1:
a.
$a^3-a^2c+a^2b-abc=a^2(a-c)+ab(a-c)$
$=(a-c)(a^2+ab)=(a-c)a(a+b)=a(a-c)(a+b)$
b.
$(x^2+1)^2-4x^2=(x^2+1)^2-(2x)^2=(x^2+1-2x)(x^2+1+2x)$
$=(x-1)^2(x+1)^2$
c.
$x^2-10x-9y^2+25=(x^2-10x+25)-9y^2$
$=(x-5)^2-(3y)^2=(x-5-3y)(x-5+3y)$
d.
$4x^2-36x+56=4(x^2-9x+14)=4(x^2-2x-7x+14)$
$=4[x(x-2)-7(x-2)]=4(x-2)(x-7)$
Bài 2:
a. $(3x+4)^2-(3x-1)(3x+1)=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-[(3x)^2-1]=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-(3x)^2=48$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4-3x)(3x+4+3x)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(6x+4)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x+4=12$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x=8$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$
b. $x^2-4x+4=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-2-9)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-11)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x-11=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=11$
c.
$x^2-25=3x-15$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)=3(x-5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-5=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=5$ hoặc $x=-2$

ta có : \(m=x^2-x+1=x^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}.x+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\) với mọi \(x\)
\(\Rightarrow\) giá trị nhỏ nhất của \(m=x^2-x+1\) là \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của \(m=x^2-x+1\) là \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(=15x-3x^2+15-3x-3x^2+9x+3x+7\)
\(=24x-6x^2+22\)
-> đề sai .
Ta có:\(\left(5-x\right)\left(3x+3\right)+3x\left(x+3\right)-3x+7=15x+15-3x^2-3x+3x^2-9x-3x+7=22\)
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức không phụ thuộc vào biến x.
P/s: mình sửa đề lại nhé ^^

\(A=3x^2-12x+10\\ A=3x^2-12x+12-2\\ A=\left(3x^2-12x+12\right)-2\\ A=3\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-2\\ A=3\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot2+2^2\right)-2\\ A=3\left(x-2\right)^2-2\\ Do\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\ \Rightarrow3\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\ \Rightarrow A=3\left(x-2\right)^2-2\ge-2\forall x\\ \text{Dấu “=” xảy ra khi : }\\ \left(x-2\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\\ \text{ Vậy }A_{\left(Min\right)}=-2\text{ khi }x=2\)
A=3x2 - 12x + 10
A= (3x2- 2.3x.2+22)-22+10
A= (3x-2)2+6 \(\ge\) +6
Vậy min A = 6 . Dấu = xảy ra khi 3x -2 = 0
3x= 2
x= \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
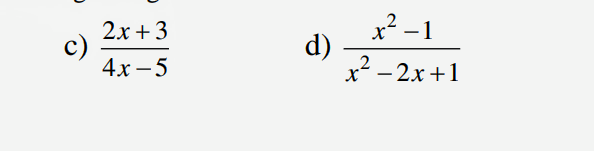


\(c,ĐK:x\ne\dfrac{5}{4}\\ \dfrac{2x+3}{4x-5}=0\Leftrightarrow2x+3=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\ d,ĐK:x\ne1\\ \dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2-2x+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
c, ĐK:x khác 5/4
Ta có 2x+3/4x-5=0=> 2x +3 =0=> x=-3/5
d, ta có x^2-1/x^2-2x+1=x+1/x-1 (ĐK : x khác 1)
Để x^2-1/x^2-2x+1=0 =>x+1/x-1=0
=>x=-1