Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) f(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 – 12x + 1 ⇒ f’(x) = 6x2 – 6x – 12
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ x ∈ {-1, 2}
So sánh các giá trị:
f(x) = -3; f(-1) = 8;
f(2) = -19, f(52)=−332f(52)=−332
Suy ra:
maxx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(−1)=8minx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(2)=−19maxx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(−1)=8minx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(2)=−19
b) f(x) = x2 lnx ⇒ f’(x)= 2xlnx + x > 0, ∀ x ∈ [1, e] nên f(x) đồng biến.
Do đó:
maxx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(e)=e2minx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(1)=0maxx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(e)=e2minx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(1)=0
c) f(x) = f(x) = xe-x ⇒ f’(x)= e-x – xe-x = (1 – x)e-x nên:
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 1, f’(x) > 0, ∀x ∈ (0, 1) và f’(x) < 0, ∀x ∈ (1, +∞)
nên:
maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(1)=1emaxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(1)=1e
Ngoài ra f(x) = xe-x > 0, ∀ x ∈ (0, +∞) và f(0) = 0 suy ra
maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(0)=0maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(0)=0
d) f(x) = 2sinx + sin2x ⇒ f’(x)= 2cosx + 2cos2x
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ cos 2x = -cosx ⇔ 2x = ± (π – x) + k2π
⇔ x∈{−π+k2π;π3+k2π3}x∈{−π+k2π;π3+k2π3}
Trong khoảng [0,3π2][0,3π2] , phương trình f’(x) = 0 chỉ có hai nghiệm là x1=π3;x2=πx1=π3;x2=π
So sánh bốn giá trị : f(0) = 0; f(π3)=3√32;f(π)=0;f(3π2)=−2f(π3)=332;f(π)=0;f(3π2)=−2
Suy ra:
maxx∈[0,3π2]f(x)=f(π3)=3√32minx∈[0,3π2]f(x)=f(3π2)=−2

\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}=\dfrac{2\left(x-3\right)+5}{x-3}=1+\dfrac{5}{\left(x-3\right)}\)
f(x) có dạng \(y=\dfrac{5}{x}\Rightarrow\) f(x) luôn nghịch biến
Tất nhiên bạn có thể tính đạo hàm --> f(x) <0 mọi x khác -3
f(x) luôn nghich biến [0;2] < -3 thuộc nhánh Bên Phải tiệm cận đứng
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}Max=f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\\Min=f\left(2\right)=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)


bn ơi câu a t chưa làm chưa biết nhưng câu b chắc chắn có Max tại x=-3 nhé ! Nếu bn chỉ tìm ra Min là chưa đủ

1. \(f\left(x\right)=e^{2-3x}\) trên đoạn \(\left[0;2\right]\)
Ta có :
\(f'\left(x\right)=-3e^{2-3x}< 0\) với \(x\in R\Rightarrow\) hàm số nghịch biến trên đoạn \(\left[0;2\right]\)
Với \(0\le x\le2\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)\ge f\left(x\right)\ge f\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow e^2\ge f\left(x\right)\ge\frac{1}{e^4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}Max_{x\in\left[0;2\right]}f\left(x\right)=e^2;x=0\\Min_{x\in\left[0;2\right]}f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{e^4};x=2\end{cases}\)
2. \(f\left(x\right)=e^{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\) trên đoạn \(\left[-1;1\right]\)
Ta có :
\(f'\left(x\right)=\frac{-x}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}e^{\sqrt{1-x^2}}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Mà : \(\begin{cases}f\left(-1\right)=1\\f\left(0\right)=e\\f\left(1\right)=1\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}Max_{x\in\left[-1;1\right]}f\left(x\right)=e;x=0\\Min_{x\in\left[-1;1\right]}f\left(x\right)=1;x=\pm1\end{cases}\)

1. \(f\left(x\right)=e^{x^3-3x+3}\) trên đoạn \(\left[0;2\right]\)
Ta có : \(f'\left(x\right)=\left(3x^2-3\right)e^{x^3-3x+3}=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=-1\notin\left[0;2\right]\\x=1\in\left[0;2\right]\end{array}\right.\)
mà : \(\begin{cases}f\left(0\right)=e^3\\f\left(1\right)=e\\f\left(2\right)=e^5\end{cases}\) \(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}Max_{x\in\left[0;2\right]}f\left(x\right)=e^5;x=1\\Min_{x\in\left[0;2\right]}f\left(x\right)=e;x=2\end{cases}\)
2. \(f\left(x\right)=\ln\left(x^2-x+1\right)\) trên đoạn \(\left[1;3\right]\)
Mà \(\begin{cases}f\left(1\right)=0\\f\left(3\right)=\ln7\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}Max_{x\in\left[1;3\right]}f\left(x\right)=\ln7;x=3\\Min_{x\in\left[1;3\right]}f\left(x\right)=0;x=1\end{cases}\)
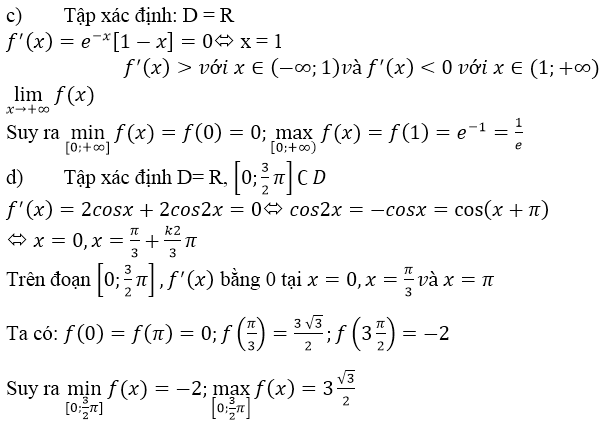
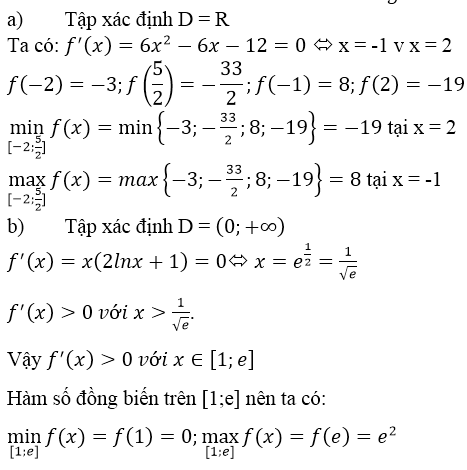



Đáp án B