Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bàii làm
a) ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = x2 - 4
<=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = x2 - 4
<=> x2 - x2 - 5x + 6 - 4 = 0
<=> -5x + 2 = 0
<=> -5x = -2
<=> x = 2/5
Vậy x = 2/5 là nghiệm phương trình.
b) \(\frac{x+2}{x-2}-\frac{1}{x}=\frac{x+6}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
=> x( x + 2 ) - ( x - 2 ) = x + 6
<=> x2 + 2x - x + 2 - x - 6 = 0
<=> x2 - 4 = 0
<=> x2 = 4
<=> x = + 4
Vậy nghiệm S = { + 4 }
c) \(\frac{2x-1}{-3}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-1}{-3}.\left(-3\right)< 1\left(-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1< -3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x< -2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
Vậy nghiệm bất phương trình S = { x / x < -1 }
d) ( x - 1 )2 < 5 - 2x
<=> x2 - 2x + 1 < 5 - 2x
<=> x2 - 2x + 1 - 5 + 2x < 0
<=> x2 - 4 < 0
<=> x2 < 4
<=> x < + 2
Vậy tập nghiệm S = { x / x < +2 }

a) \(\frac{x-1}{2}+\frac{x-2}{3}+\frac{x-3}{4}=\frac{x-4}{5}+\frac{x-5}{6}\)
\(\left(\frac{x-1}{2}+1\right)+\left(\frac{x-2}{3}+3\right)+\left(\frac{x-3}{4}+1\right)=\left(\frac{x-4}{5}+1\right)+\left(\frac{x-5}{6}+1\right)\)
\(\frac{x-1}{2}+\frac{x-1}{3}+\frac{x-1}{4}=\frac{x-1}{5}+\frac{x-1}{6}\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{6}\right)\)=0
\(x-1=0\)
\(x=1\)

(x2-5x+1)(x2-4)=6(x-1)2
<=>(x2-5x+1)(x2-4)-6(x-1)2=0
<=>x4-5x3-3x2+20x-4-6x2+12x-6=0
<=>x4-5x3-9x2+32x-10=0
<=>x4-6x3+2x2+x3-6x2+2x-5x2+30x-10=0
<=>x2(x2-6x+2)+x(x2-6x+2)-5(x2-6x+2)=0
<=>(x2-6x+2)(x2+x-5)=0
- Với x2-6x+2=0 <=>x2-6x+9-7=0
<=>(x-3)2-7=0
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=-\sqrt{7}hoac\sqrt{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\pm\sqrt{7}\)
- Với x2+x-5=0 <=>\(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{21}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=\frac{21}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}hoac\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\)
b)\(x+\frac{1}{x}=x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\)
tính mẫu ra rồi rút gọn,x=1

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\left\{0;-1;-2;-3;-4;-5;-6;-7\right\}\)
\(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x+5}+\frac{1}{x+7}=\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x+3}+\frac{1}{x+4}+\frac{1}{x+6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+7}+\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x+5}=\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x+6}+\frac{1}{x+3}+\frac{1}{x+4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x+7+x}{x\left(x+7\right)}+\frac{x+5+x+2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x+6+x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+6\right)}+\frac{x+4+x+3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x+7}{x^2+7x}+\frac{2x+7}{x^2+7x+10}=\frac{2x+7}{x^2+7x+6}+\frac{2x+7}{x^2+7x+12}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x+7\right)\left(\frac{1}{x^2+7x}+\frac{1}{x^2+7x+10}-\frac{1}{x^2+7x+6}-\frac{1}{x^2+7x+12}\right)=0\)
mà \(\frac{1}{x^2+7x}+\frac{1}{x^2+7x+10}-\frac{1}{x^2+7x+6}-\frac{1}{x^2+7x+12}\ne0\)
=> 2x + 7 = 0 => x = -7/2
Vậy x = -7/2

\(a,\Leftrightarrow5\left(x-2\right)-15x\le9+10\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-10-15x\le9+10x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20x\le29\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1,45\)
Vậy ...........
\(b,\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)-3\left(x-3\right)=5\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2-3x+9-5x+10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7x+21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Vậy ..............
\(\frac{x-2}{6}-\frac{x}{2}\le\frac{3}{10}+\frac{x+1}{3}\Leftrightarrow\frac{5\left(x-2\right)}{30}-\frac{15x}{30}\le\frac{9}{30}+\frac{10\left(x+1\right)}{30}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-10-15x-9-10x-10\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20x-29\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(-20x\right)\cdot\frac{-1}{20}\ge29\cdot-\frac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\frac{29}{20}\)

\(\frac{1}{2-x}+1=\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{6-x}{3x^2-12}\)ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne\pm2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-3\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{3\left(x-2\right)}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{x-6}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-3x-6+3\left(x^2-4\right)}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{3x-6+x-6}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-3x-6+3x^2-12-3x+6-x+6}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-7x-6+3x^2}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-7x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-9x+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{-2}{3}\end{cases}}\)( thỏa mãn )
Vậy....
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 1 hoặc x = -1.
Ta có: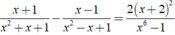
⇔ 8x = - 10 ⇔ x = - 5/4.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm là x = - 5/4.