
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



MIK giải đc nhưng ngại lắm , mỏi tay ,đáp số nè:
\(\left(x^2-x-1\right)\left(2x^2+5x-2\right)\)

Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử bằng phương pháp đặt nhân tử chung
(3x + 2)^2 + (3x - 2)^2 - 2(9x^2 - 4)
\(=\left(3x+2\right)^2-2\left(3x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)+\left(3x-2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x+2-\left(3x-2\right)\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x+2-3x+2\right)^2\)
\(=4^2\)
\(=16\)
\(\left(3x+2\right)^2+\left(3x-2\right)^2-2\left(9x^2-4\right)\)
\(=\left(3x+2\right)^2+\left(3x-2\right)^2-2.\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(3x+2-3x+2\right)^2\)
\(=4^2=16\)

\(\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(x^2-9x+20\right)-40=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)-40\)
\(=\left(x^2-6x+5\right)\left(x^2-6x+8\right)-40\)
Đặt \(t=x^2-6x+5\) thì ta có \(t\left(t+3\right)-40=t^2+3t-40=\left(t+8\right)\left(t-5\right)\)
Suy ra \(\left(x^2-6x+5\right)\left(x^2-6x+8\right)-40=\left(x^2-6x+13\right)\left(x^2-6x\right)=x\left(x-6\right)\left(x^2-6x+13\right)\)


Đặt \(P\left(x\right)=2x^4+3x^3-9x^2-3x+2\)
Giả sử nhân tử của P(x) có dạng : \(P\left(x\right)=2\left(x^2+ax+b\right)\left(x^2+cx+d\right)=\left(x^2+ax+b\right)\left(2x^2+2cx+2d\right)\)
Khai triển : \(P\left(x\right)=2x^4+2cx^3+2dx^2+2ax^3+2acx^2+2adx+2bx^2+2bcx+2bd\)
\(=2x^4+x^3\left(2c+2a\right)+x^2\left(2d+2ac+2b\right)+x\left(2ad+2cb\right)+2bd\)
Dùng phương pháp hệ số bất định :
\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}2a+2c=3\\2ac+2b+2d=-9\\2ad+2bc=-3\\bd=1\end{cases}\) . Giải ra được \(\begin{cases}a=-1\\b=-1\\c=\frac{5}{2}\\d=-1\end{cases}\)
Vậy \(P\left(x\right)=2\left(x^2-x-1\right)\left(x^2+\frac{5}{2}x-1\right)=\left(x^2-x-1\right)\left(2x^2+5x-2\right)\)

\(3x^2-6x+9x^2=12x^2-6x=6x\left(2x-1\right)\)


a) \(x^3+9x^2+27x+27=\left(x+3\right)^3\)
b) \(3\sqrt{3x^3}+18x^2+12\sqrt{3x}+8=\left(\sqrt{3x}+2\right)^3\)
c) \(\dfrac{1}{4}-x^2=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+x\right)\)
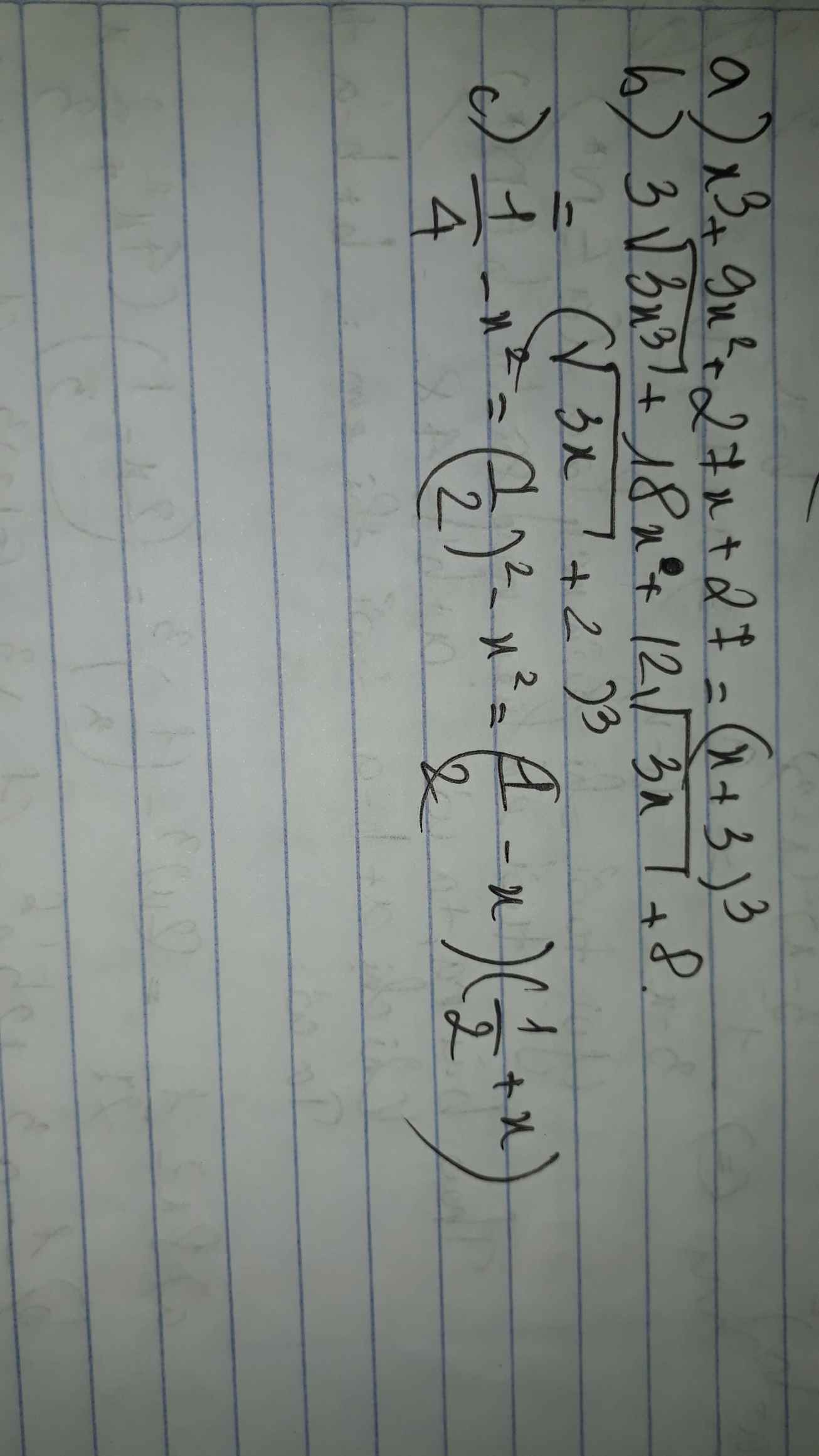
=(3x+2)^2+(3x-2)^2-2(3x-2)(3x+2)
=(3x+2-3x+2)^2
=4^2
=16