
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a. \(\int\dfrac{x^3}{x-2}dx=\int\left(x^2+2x+4+\dfrac{8}{x-2}\right)dx=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3+x^2+4x+8ln\left|x-2\right|+C\)
b. \(\int\dfrac{dx}{x\sqrt{x^2+1}}=\int\dfrac{xdx}{x^2\sqrt{x^2+1}}\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2+1}=u\Rightarrow x^2=u^2-1\Rightarrow xdx=udu\)
\(I=\int\dfrac{udu}{\left(u^2-1\right)u}=\int\dfrac{du}{u^2-1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{u-1}-\dfrac{1}{u+1}\right)du=\dfrac{1}{2}ln\left|\dfrac{u-1}{u+1}\right|+C\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}ln\left|\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+1}-1}{\sqrt{x^2+1}+1}\right|+C\)
c. \(\int\left(\dfrac{5}{x}+\sqrt{x^3}\right)dx=\int\left(\dfrac{5}{x}+x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}\right)dx=5ln\left|x\right|+\dfrac{2}{5}\sqrt{x^5}+C\)
d. \(\int\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}}{x^2}dx=\int\left(x^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}+x^{-\dfrac{3}{2}}\right)dx=2\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}+C\)
e. \(\int\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}=arcsin\left(x\right)+C\)

Chọn C.
Đặt u = G ( x ) d v = f ( x ) d x ⇒ d u = G ( x ) ' d x = g ( x ) d x v = ∫ f ( x ) d x = F ( x )
Suy ra: I = G ( x ) F ( x ) 2 0 - ∫ 0 2 F ( x ) g ( x ) d x
= G(2)F(2) – G(0)F(0) – 3 = 1 – 0 – 3 = -2.

Lời giải:
Đặt \(u=\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1}); dv=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx\)
\(\Rightarrow du=\frac{dx}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}; v=\int \frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\int \frac{d(x^2+1)}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}=\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow \int \frac{x\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx=\int udv=uv-vdu=\sqrt{x^2+1}\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})-\int dx\)
\(=\sqrt{x^2+1}\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})-x+C\)

a) Mẫu số chứa các biểu thức có nghiệm thực và không có nghiệm thực.
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2+2x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{Bx+C}{x^2+1}=\frac{A\left(x^2+1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(Bx+C\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\left(1\right)\)
Tay x=1 vào 2 tử, ta có : 2=2A, vậy A=1
Do đó (1) trở thành :
\(\frac{1\left(x^2+1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(Bx+C\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}=\frac{\left(B+1\right)x^2+\left(C-B\right)x+1-C}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
Đồng nhất hệ số hai tử số, ta có hệ :
\(\begin{cases}B+1=1\\C-B=2\\1-C=-1\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\begin{cases}B=0\\C=2\\A=1\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\)
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x-1}+\frac{2}{x^2+1}\)
Vậy :
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2+2x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}dx=\int\frac{1}{x-1}dx+2\int\frac{1}{x^2+1}=\ln\left|x+1\right|+2J+C\left(2\right)\)
* Tính \(J=\int\frac{1}{x^2+1}dx.\)
Đặt \(\begin{cases}x=\tan t\rightarrow dx=\left(1+\tan^2t\right)dt\\1+x^2=1+\tan^2t\end{cases}\)
Cho nên :
\(\int\frac{1}{x^2+1}dx=\int\frac{1}{1+\tan^2t}\left(1+\tan^2t\right)dt=\int dt=t;do:x=\tan t\Rightarrow t=arc\tan x\)
Do đó, thay tích phân J vào (2), ta có :
\(\int\frac{x^2+2x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}dx=\ln\left|x-1\right|+arc\tan x+C\)
b) Ta phân tích
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2+1}{\left(x-1\right)^3\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{A}{\left(x-1\right)^3}+\frac{B}{\left(x-1\right)^2}+\frac{C}{x-1}+\frac{D}{x+3}\)\(=\frac{A\left(x+3\right)+B\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)+C\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+3\right)+D\left(x-1\right)^3}{\left(x-1\right)^3\left(x+3\right)}\)
Thay x=1 và x=-3 vào hai tử số, ta được :
\(\begin{cases}x=1\rightarrow2=4A\rightarrow A=\frac{1}{2}\\x=-3\rightarrow10=-64D\rightarrow D=-\frac{5}{32}\end{cases}\)
Thay hai giá trị của A và D vào (*) và đồng nhất hệ số hai tử số, ta cso hệ hai phương trình :
\(\begin{cases}0=C+D\Rightarrow C=-D=\frac{5}{32}\\1=3A-3B+3C-D\Rightarrow B=\frac{3}{8}\end{cases}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)^3}+\frac{3}{8\left(x-1\right)^2}+\frac{5}{32\left(x-1\right)}-+\frac{5}{32\left(x+3\right)}\)
Vậy :
\(\int\frac{x^2+1}{\left(x-1\right)^3\left(x+3\right)}dx=\)\(\left(\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)^3}+\frac{3}{8\left(x-1\right)^2}+\frac{5}{32\left(x-1\right)}-+\frac{5}{32\left(x+3\right)}\right)dx\)
\(=-\frac{1}{a\left(x-1\right)^2}-\frac{3}{8\left(x-1\right)}+\frac{5}{32}\ln\left|x-1\right|-\frac{5}{32}\ln\left|x+3\right|+C\)
\(=-\frac{1}{a\left(x-1\right)^2}-\frac{3}{8\left(x-1\right)}+\frac{5}{32}\ln\left|\frac{x-1}{x+3}\right|+C\)

a)
\(\int\frac{2\left(x_{ }+1\right)}{x^2+2x_{ }-3}dx=\int\frac{2x+2}{x^2+2x-3}dx\)
\(=\int\frac{d\left(x^2+2x-3\right)}{x^2+2x-3}=ln\left|x^2+2x-3\right|+C\)
b)\(\int\frac{2\left(x-2\right)dx}{x^2-4x+3}=\int\frac{2x-4dx}{x^2-4x+3}=\int\frac{d\left(x^2-4x+3\right)}{x^2-4x+3}=ln\left|x^2-4x+3\right|+C\)
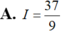
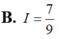
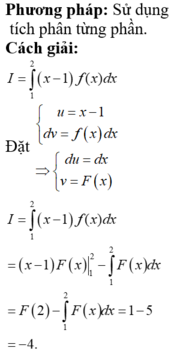
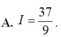
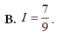
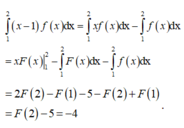

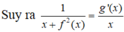
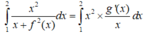
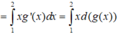
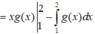
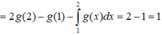
\(\int\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{x^2}dx=\int\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)dx=x+ln\left|x\right|-\dfrac{1}{x}+C\)