Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(cos^4x-sin^4x=sin3x+cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cos^2x+sin^2x\right)\left(cos^2x-sin^2x\right)=sin3x+cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x=sin3x+cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos4x-cos2x+sin3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2sin3x.sinx+sin3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin3x\left(1-2sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin3x=0\\sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{0;\dfrac{\pi}{3};\dfrac{2\pi}{3};\pi;\dfrac{\pi}{6};\dfrac{5\pi}{6}\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sum x=3\pi\)

\(1-2cos^2x-sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2\left(1-sin^2x\right)-sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x-sinx-1=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=1\\sinx=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{\dfrac{\pi}{2};\dfrac{7\pi}{6};\dfrac{11\pi}{6};\dfrac{5\pi}{2}\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sum x=6\pi\)

Chọn D

Bổ trợ kiến thức: Ở những dạng toán trên ta khó có thể biến đổi để xử lí trên máy tính cầm tay, có lẽ ở đây ra nên sử dụng hình thức tự luận để giải quyết một bài toán trắc nghiệm không quá khó khăn. Học sinh cần ghi nhớ một số công thức được sử dụng trong bài toán trên: ![]()

ta có \(\hept{\begin{cases}\sqrt{2}\left(sinx+cosx\right)=2sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\\sinx.cosx=\frac{1}{2}sin2x=-\frac{1}{2}cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=-\frac{1-2sin^2\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy phương trình \(\Leftrightarrow2sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+\frac{1-2sin^2\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)}{2}=1\)
Đặt \(sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=a\Rightarrow PT\Leftrightarrow2a+\frac{1-2a^2}{2}=1\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a=1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\\a=1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\end{cases}}\)
vì sin <1 nên \(sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)có 4 nghiệm trên \(\left(0,2\pi\right)\)

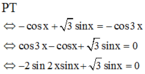
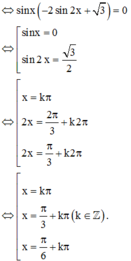
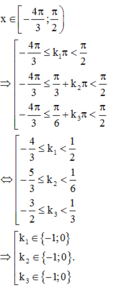
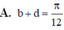
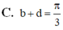


Lời giải:
\(\sin 3x=-\sin x=\sin (-x)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} 3x=-x+2k\pi\\ 3x=\pi +x+2t\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) với $t,k$ nguyên bất kỳ
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x=\frac{k\pi}{2}\\ x=\frac{(2t+1)\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) với $k,t$ nguyên bất kỳ
Để $x\in [0; 100\pi]$ thì \(\left\{\begin{matrix} 0\leq \frac{k}{2}\leq 100\\ 0\leq \frac{2t+1}{2}\leq 100\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì $t,k$ nguyên nên:
$k\in \left\{0;1;2;...;200\right\}$ $\rightarrow 201$ giá trị
$t\in \left\{0;1;2;,,,;99\right\}$ $\rightarrow 100$ giá trị
Vậy có: $201+100=301$ nghiệm.
Em cảm mơn nhiều ạ