
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

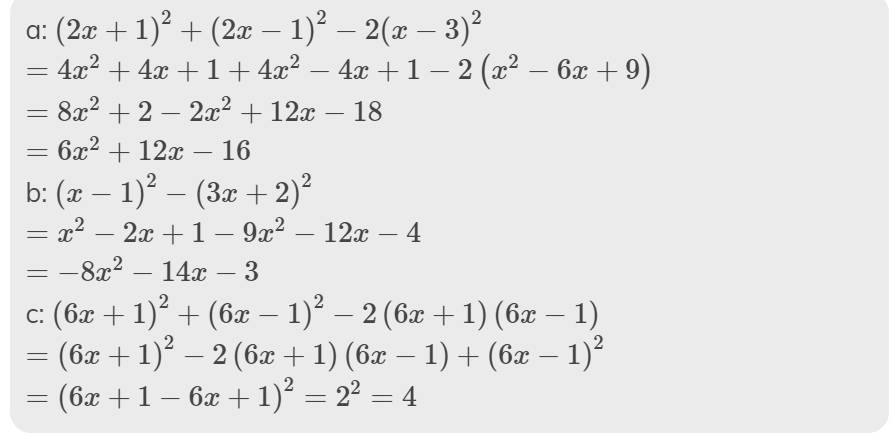

Bài 1:
a) (3x-2).(4x+5)-6x.(2x-1) = 12x^2 +15x - 8x -10 - 12x^2 + 6x = 13x - 10
b) (2x-5)^2 - 4.(x+3).(x-3) = 4x^2 - 20x + 25 - 4x^2 + 12x -12x + 36 = -20x + 61
Bài 2:
a)(2x-1)^2-(x+3)^2 = 0
<=> (2x-1-x-3).(2x-1+x+3) =0
<=>(x-4).(3x+2) = 0
<=> x-4 = 0 hoặc 3x+2=0
*x-4=0 => x=4
*3x+2 = 0 => 3x=-2 => x=-2/3
b)x^2(x-3)+12-4x=0 <=> x^2(x-3) - 4(x-3) =0 <=> (x-3).(x-2)(x+2) <=> x-3=0 hoặc x-2=0 hoặc x+2 =0
*x-3=0 => x=3
*x-2=0 =>x=2
*x+2=0 =>x=-2
c) 6x^3 -24x =0 <=> 6x(x^2 -4)=0 <=> 6x(x-2)(x+2)=0 <=> x=0 hoặc x-2 =0 hoặc x+2=0 <=> x=0 hoặc x=2 hoặc x=-2

Bài 1: mình ko bik yêu cầu đề bài nên mình ko làm.
Bài 2:
a/ \(\left(2x+5\right)^2=\left(2x\right)^2+2.2x.5+5^2\)
\(=4x^2+20x+25\)
b/ \(\left(3x+4\right)^2=\left(3x\right)^2+2.3x.4+4^2\)
\(=9x^2+24x+16\)
c/\(\left(3x+5y+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
Đối với bình phương của một tổng gồm ba hạng tử, ta có công thức như sau:
(a+b+c)2=a2+b2+c2+2ab+2ac+2bc=a2+b2+c2+2(ab+bc+ac)
\(\left(3x+5y+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=9x^2+25y^2+\frac{1}{4}+2\left(15x+\frac{3x}{2}+\frac{5y}{2}\right)\)
Bài 3:
a/ A= x2+10x+30
A= x2+2.5x+25+5
A= x2+2.5.x+52+5
A=(x+5)2+5
Ta có (x+5)2 luôn luôn > hoặc = 0
=>(x+5)2+5 luôn luôn lớn hơn 0 (vì 5>0)
=> A luôn dương.
b/ \(B=3x^2+6x+19\\ B=\left(\sqrt{3x}\right)^2+2x.\sqrt{3}.\sqrt{3}+3+16\)
\(B=\left(\sqrt{3x}+\sqrt{3}\right)^2+16\)
(Tương tự như câu A)
Ta có \(\left(\sqrt{3x}+\sqrt{3}\right)^2\)luôn luôn > hoặc = 0
=> \(\left(\sqrt{3x}+\sqrt{3}\right)^2+16\) luôn luôn > 0 (vì 16 > 0)
=> B luôn dương.
c/ \(C=4x^2+10x+32\\ C=\left(2x\right)^2+2.2x.\frac{5}{2}+\frac{25}{4}+\frac{103}{4}\\C=\left(2x+\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{103}{4} \)
(Chứng minh tương tự câu a, b)
Chúc bạn học tốt!!
mk giúp bạn bài 3 còn bài 1, 2 tự làm nha
a , A = x2 + 10x +30
= (x2 + 2 . 5 . x +52 ) +5
= (x+5)2 + 5
Vì (x+5)2 >= 0 (luôn đúng)
=> (x+5)2 + 5 luôn luôn dương

1. <=> \(\left(3x+2\right)^3-\left(\left(3x\right)^3+2^3\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(\left(3x\right)^3+2^3+3\left(3x+2\right).3x.2\right)-\left(\left(3x\right)^3+2^3\right)=0\)
<=>3 (3x + 2) . 3x.2 = 0
<=> (3x + 2 ) . x = 0
<=> x = -2/3 hoặc x = 0
2. Tương tự
1
\(\left(3x+2\right)^3-\left[\left(3x\right)^3+2^3\right]=0\)
\(\left(3x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(3x\right)^2\cdot2+3\cdot3x\cdot2^2+2^3-\left(3x\right)^3-2^3=0\)
\(54x^2+36x=0\)
\(18x\left(3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-2}{3}\end{cases}}\)
2
\(\left(2x+1\right)^3-\left[\left(2x\right)^3-1^3\right]=0\)
\(\left(2x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(2x\right)^2\cdot1+3\cdot2x\cdot1^2+1^3-\left(2x\right)^3-1^3=0\)
\(12x^2+6x=0\)
\(6x\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\2x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-1}{2}\end{cases}}\)

\(A=x^2-6x+10=x^2-2.3x+3^2+1=\left(x-3\right)^2+1\)
Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2\ge0\) nên \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge1\)
Vậy \(A_{min}=1\)(Dấu "="\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\))
a) \(\left(x+1\right)^3-x^2\left(x+3\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+3x^2+3x+1\right)-\left(x^3+3x^2\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3-3x^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+1=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}\)

Đề bài là giải các phương trình nha :Đ
\(b,\left(2x+1\right)^2=9\)
\(\left(2x+1\right)^2=3^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+1=3\\2x+1=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=2\\2x=-4\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\end{cases}}}\)
\(c,x^3+5x^2-4x-20=0\)
\(x^2\left(x+5\right)-4\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-4=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=4\\x=5\end{cases}}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-2\end{cases};x=5}\)
ko phải mk lười đâu , cái này bn làm nó mới có ý nghĩa , cố gắng nốt nha !

a) \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-3\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=\left(x-2\right)^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-3\left(x^2-16\right)=x^2-4x+4+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-3x^2+48=x^2-4x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+12x+57=x^2-4x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x+52=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{13}{4}\)
b) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(9x^2+6x+4\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2-3x+1\right)=x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)Xem lại đề !
c) \(x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+4\right)=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-x^2-x+12=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+12=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{12}{7}\)
d) \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=4x\left(x-7\right)-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-1=4x^2-28x-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow28x+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow31x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{31}\)

3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
<=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
<=> 3x ( x + 1 ) - ( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 1 ) ( 3x -1 ) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
KL : Tập nghiệp ...........................
\(3x^2+2x-1=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=2^2+4.3.1=16,\sqrt{\Delta}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-2+4}{6}=\frac{1}{3}\\x=\frac{-2-4}{6}=-1\end{cases}}\)

a) x2 - 4x + 2 = (x2 - 4x + 4) - 2 = (x - 2)2 - 2 = \(\left(x-2+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x-2-\sqrt{2}\right)\)
b) x2 - 12x + 11 = x2 - x - 11x + 11 = x(x - 1) - 11(x - 1) = (x - 1)(x - 11)
c) 3x2 + 6x - 9 = 3x2 - 3x + 9x - 9 = 3x(x - 1) + 9(x - 1) = (3x + 9)(x - 1) = 3(x + 3)(x - 1)
d) 2x2 - 6x + 2 = 2(x2 - 3x + 1) = 2(x2 - 3x + 9/4 - 5/4) = 2[(x - 3/2)2 - 5/4] = \(2\left(x-\frac{3}{2}+\sqrt{\frac{5}{4}}\right)\left(x-\frac{3}{2}-\sqrt{\frac{5}{4}}\right)\)
1.
a) \(x^2-4x+2=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-2=\left(x-2\right)^2-2=\left(x-2-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x-2+\sqrt{2}\right)\)
b) \(x^2-12x+11=\left(x^2-12x+36\right)-25=\left(x-6\right)^2-5^2=\left(x-6-5\right)\left(x-6+5\right)=\left(x-11\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
c) \(3x^2+6x-9=3\left(x^2+2x-3\right)=3\left[\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-4\right]=3\left[\left(x+1\right)^2-2^2\right]=3\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
d) \(2x^2-6x+2=2\left(x^2-3x+1\right)=2\left(x^2-2.x.\frac{3}{2}+\frac{9}{4}-\frac{5}{4}\right)=2\left[\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2-\frac{5}{4}\right]\)
\(=2\left(x-\frac{3}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)\left(x-\frac{3}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)\)

Ta có:
\(A=\left(3x-5\right)\left(2x+11\right)-\left(2x+3\right)\left(3x+7\right)\)
\(=\left[3x\left(2x+11\right)-5\left(2x+11\right)\right]-\left[2x\left(3x+7\right)+3\left(3x+7\right)\right]\)
\(=\left[\left(6x^2+33x\right)-\left(10x+55\right)\right]-\left[\left(6x^2+14x\right)+\left(9x+21\right)\right]\)
\(=\left[6x^2+23x-55\right]-\left[6x^2+23x+21\right]\)
\(=-55-21=-76\)
Vậy biểu thức A không phụ thuộc vào biến x, y.

Bài 1.
a) x( 8x - 2 ) - 8x2 + 12 = 0
<=> 8x2 - 2x - 8x2 + 12 = 0
<=> 12 - 2x = 0
<=> 2x = 12
<=> x = 6
b) x( 4x - 5 ) - ( 2x + 1 )2 = 0
<=> 4x2 - 5x - ( 4x2 + 4x + 1 ) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 5x - 4x2 - 4x - 1 = 0
<=> -9x - 1 = 0
<=> -9x = 1
<=> x = -1/9
c) ( 5 - 2x )( 2x + 7 ) = ( 2x - 5 )( 2x + 5 )
<=> -4x2 - 4x + 35 = 4x2 - 25
<=> -4x2 - 4x + 35 - 4x2 + 25 = 0
<=> -8x2 - 4x + 60 = 0
<=> -8x2 + 20x - 24x + 60 = 0
<=> -4x( 2x - 5 ) - 12( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> ( 2x - 5 )( -4x - 12 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\-4x-12=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{cases}}\)
d) 64x2 - 49 = 0
<=> ( 8x )2 - 72 = 0
<=> ( 8x - 7 )( 8x + 7 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}8x-7=0\\8x+7=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{7}{8}\\x=-\frac{7}{8}\end{cases}}\)
e) ( x2 + 6x + 9 )( x2 + 8x + 7 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2( x2 + x + 7x + 7 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2 [ x( x + 1 ) + 7( x + 1 ) ] = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )2( x + 1 )( x + 7 ) = 0
<=> x = -3 hoặc x = -1 hoặc x = -7
g) ( x2 + 1 )( x2 - 8x + 7 ) = 0
Vì x2 + 1 ≥ 1 > 0 với mọi x
=> x2 - 8x + 7 = 0
=> x2 - x - 7x + 7 = 0
=> x( x - 1 ) - 7( x - 1 ) = 0
=> ( x - 1 )( x - 7 ) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-7=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=7\end{cases}}\)
Bài 2.
a) ( x - 1 )2 - ( x - 2 )( x + 2 )
= x2 - 2x + 1 - ( x2 - 4 )
= x2 - 2x + 1 - x2 + 4
= -2x + 5
b) ( 3x + 5 )2 + ( 26x + 10 )( 2 - 3x ) + ( 2 - 3x )2
= 9x2 + 30x + 25 - 78x2 + 22x + 20 + 9x2 - 12x + 4
= ( 9x2 - 78x2 + 9x2 ) + ( 30x + 22x - 12x ) + ( 25 + 20 + 4 )
= -60x2 + 40x2 + 49
d) ( x + y )2 - ( x + y - 2 )2
= [ x + y - ( x + y - 2 ) ][ x + y + ( x + y - 2 ) ]
= ( x + y - x - y + 2 )( x + y + x + y - 2 )
= 2( 2x + 2y - 2 )
= 4x + 4y - 4
Bài 3.
A = 3x2 + 18x + 33
= 3( x2 + 6x + 9 ) + 6
= 3( x + 3 )2 + 6 ≥ 6 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x + 3 = 0 => x = -3
=> MinA = 6 <=> x = -3
B = x2 - 6x + 10 + y2
= ( x2 - 6x + 9 ) + y2 + 1
= ( x - 3 )2 + y2 + 1 ≥ 1 ∀ x,y
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\y^2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=0\end{cases}}\)
=> MinB = 1 <=> x = 3 ; y = 0
C = ( 2x - 1 )2 + ( x + 2 )2
= 4x2 - 4x + 1 + x2 + 4x + 4
= 5x2 + 5 ≥ 5 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> 5x2 = 0 => x = 0
=> MinC = 5 <=> x = 0
D = -2/7x2 - 8x + 7 ( sửa thành tìm Max )
Để D đạt GTLN => 7x2 - 8x + 7 đạt GTNN
7x2 - 8x + 7
= 7( x2 - 8/7x + 16/49 ) + 33/7
= 7( x - 4/7 )2 + 33/7 ≥ 33/7 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x - 4/7 = 0 => x = 4/7
=> MaxC = \(\frac{-2}{\frac{33}{7}}=-\frac{14}{33}\)<=> x = 4/7