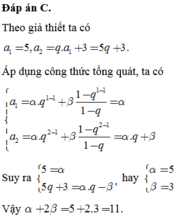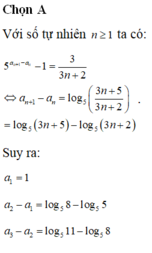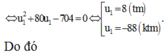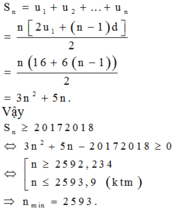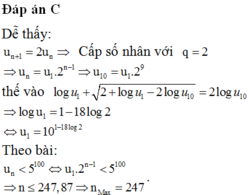Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(21+22+23+...+n+4840\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[\left(n-21\right):1+1\right]\left(n+21\right):2=4840\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(n-20\right)\left(n+21\right)=9680\)
\(\Rightarrow n^2+n-420=9680\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^2+n-100100=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^2-100n+101n-100100=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n\left(n-100\right)+101\left(n-100\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(n+101\right)\left(n-100\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[n=-101\text{(loại)},n=100\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow n=100\)
\(\text{Hok tốt!}\)
\(\text{@Kaito Kid}\)
21 + 22 + 23 + ... + n = 4840
=> [(n - 21) : 1 + 1](n + 21) : 2 = 4840
=> (n - 20)(n + 21) = 9680
=> n2 + n - 420 = 9680
<=> n2 + n - 10100 = 0
<=> n2 - 100n + 101n - 10100 = 0
<=> n(n - 100) + 101(n - 100) = 0
<=> (n + 101)(n - 100) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}n=-101\left(\text{loại}\right)\\n=100\end{cases}}\)
Vậy n = 100


\(logu_1+\sqrt{2+logu_1-2logu_{10}}=2logu_{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow logu_1-2logu_{10}+\sqrt{2+logu_1-2logu_{10}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-2+t=0\)(\(t=\sqrt{2+logu_1-2logu_{10}}\ge0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=1\\t=-2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow2+logu_1-2logu_{10}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2+logu_1-2log\left(2^9u_1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log\left(10u_1\right)=log\left(2^9u_1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow10u_1=2^{18}u_1^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_1=\frac{10}{2^{18}}\).
\(u_n=\frac{2^{n-1}.10}{2^{18}}>5^{100}\Leftrightarrow n>log_2\left(\frac{5^{100}.2^{19}}{10}\right)=-log_210+100log_25+19\)
Suy ra \(n\ge248\).

Chọn A
Với số tự nhiên n ≥ 1, ta có:
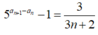
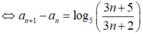
![]()
Suy ra:
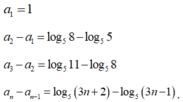
Cộng tương ứng hai vế các đẳng thức trên ta có ![]() với mọi số tự nhiên n
≥
1
với mọi số tự nhiên n
≥
1
Để ![]()
![]()
Ta kiểm tra với các giá trị k ∈ ℕ từ bé đến lớn
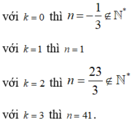
Vậy số nguyên n > 1 nhỏ nhất là n = 41( ứng với k = 3).