Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải của bạn Nhật Linh đúng rồi, tuy nhiên cần thêm điều kiện để A có nghĩa: \(x\ne\pm2\)

\(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}+\dfrac{6x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\right):\left(x+2\right)\)\(A=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
a) \(A=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-1;-2\\\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
\(A>1;\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}>1\Leftrightarrow x^2-x< 0\Leftrightarrow0< x< 1\)
\(P=\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}.\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
x>0 => P >0 đang tìm Giá trị LN => chỉ xét P>0 <=> x>0
\(\dfrac{1}{P}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x}=x+2+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
áp co si hai số dương x ; 1/x
\(\dfrac{1}{P}\ge2.\sqrt{x.\dfrac{1}{x}}+2=4\Rightarrow P\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
đẳng thức khi x =1/x => x=1 thỏa mãn đk của x
\(MaxP=\dfrac{1}{4}\)

B3;a,ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne\pm4\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{4}{x-4}-\dfrac{4}{x+4}\right)\dfrac{x^2+8x+16}{32}=\left(\dfrac{4x+16}{x^2-16}-\dfrac{4x-16}{x^2-16}\right)\dfrac{x^2+2.4x+4^2}{32}=\left(\dfrac{4x+16-4x+16}{x^2-16}\right)\dfrac{\left(x+4\right)^2}{32}=\left(\dfrac{32}{x^2-16}\right)\dfrac{\left(x+4\right)^2}{32}=\dfrac{32\left(x+4\right)^2}{32.\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{x+4}{x-4}\\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ b,Tacó\dfrac{x+4}{x-4}=\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow3x+12=x-4\Leftrightarrow x=-8\left(TM\right)c,TAcó\dfrac{x+4}{x-4}=3\Leftrightarrow x+4=3x-12\Leftrightarrow x=8\left(TM\right)\)

Câu 1 :
a) Rút gọn P :
\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{3x-x^2}:\left(\dfrac{3+x}{3-x}-\dfrac{3-x}{3+x}-\dfrac{12x^2}{x^2-9}\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x\left(3-x\right)}:\left[\dfrac{\left(3+x\right)^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}-\dfrac{\left(3-x\right)^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}-\dfrac{12x^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}\right]\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x\left(3-x\right)}:\left(\dfrac{9+6x+x^2-9+6x-x^2-12x^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x\left(3-x\right)}:\dfrac{12x-12x^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x\left(3-x\right)}.\dfrac{\left(3-x\right)\left(x+3\right)}{12x\left(1-x\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}{12x^2\left(1-x\right)}\)

\(a,A=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}\right).\left(\dfrac{2}{x}-1\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right).\left(\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{x}{x}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x^2-4x+4-x^2-4x-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right).\left(\dfrac{2-x}{x}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-8x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{x-2}{-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{8}{x+2}\)
b, Thay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\) vào biểu thức A ,có :
\(\dfrac{8}{-\dfrac{2}{5}+2}=\dfrac{8}{\dfrac{8}{5}}=5\)
Vậy tại x = -2/5 giá trị của A là 5
c, Để \(A=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8}{x+2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=14\)
Vậy x = 14 thì A = 1/2

a)
Đặt
\(\sqrt{1+x}=a; \sqrt{1-x}=b\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} ab=\sqrt{(1+x)(1-x)}=\sqrt{1-x^2}\\ a\geq b\\ a^2+b^2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó:
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{1-\sqrt{1-x^2}}(\sqrt{(1+x)^3}+\sqrt{(1-x)^3})}{2-\sqrt{1-x^2}}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{\frac{a^2+b^2}{2}-ab}(a^3+b^3)}{a^2+b^2-ab}=\frac{\sqrt{\frac{a^2+b^2-2ab}{2}}(a+b)(a^2-ab+b^2)}{a^2+b^2-ab}\)
\(=\sqrt{\frac{a^2-2ab+b^2}{2}}(a+b)=\sqrt{\frac{(a-b)^2}{2}}(a+b)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}|a-b|(a+b)\)
\(=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(a-b)(a+b)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(a^2-b^2)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[(1+x)-(1-x)]=\sqrt{2}x\)
Sửa đề: \(\frac{25}{(x+z)^2}=\frac{16}{(z-y)(2x+y+z)}\)
Ta có:
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau thì:
\(k=\frac{a}{x+y}=\frac{5}{x+z}=\frac{a+5}{2x+y+z}=\frac{5-a}{z-y}\) ($k$ là một số biểu thị giá trị chung)
Khi đó:
\(\frac{16}{(z-y)(2x+y+z)}=\frac{25}{(x+z)^2}=(\frac{5}{x+z})^2=k^2\)
Mà: \(k^2=\frac{a+5}{2x+y+z}.\frac{5-a}{z-y}=\frac{25-a^2}{(2x+y+z)(z-y)}\)
Do đó: \(\frac{16}{(z-y)(2x+y+z)}=\frac{25-a^2}{(2x+y+z)(z-y)}\Rightarrow 16=25-a^2\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2=9\Rightarrow a=\pm 3\)
Suy ra:
\(Q=\frac{a^6-2a^5+a-2}{a^5+1}=\frac{a^5(a-2)+(a-2)}{a^5+1}=\frac{(a-2)(a^5+1)}{a^5+1}=a-2=\left[\begin{matrix}
1\\
-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
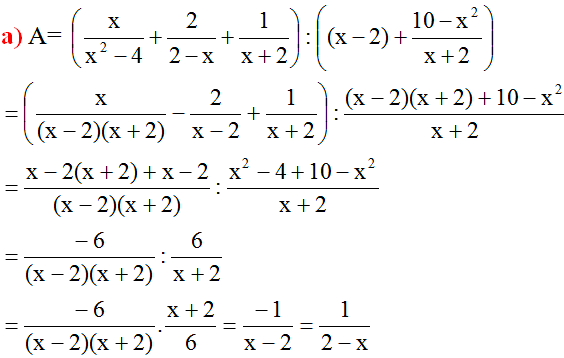
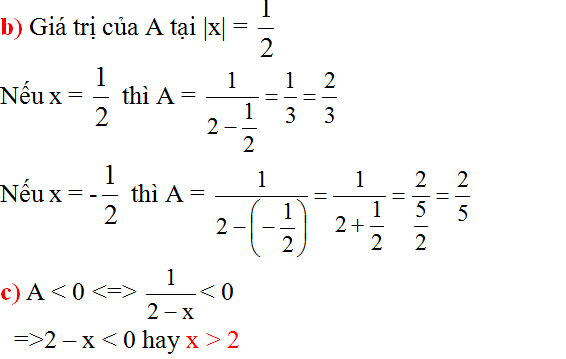



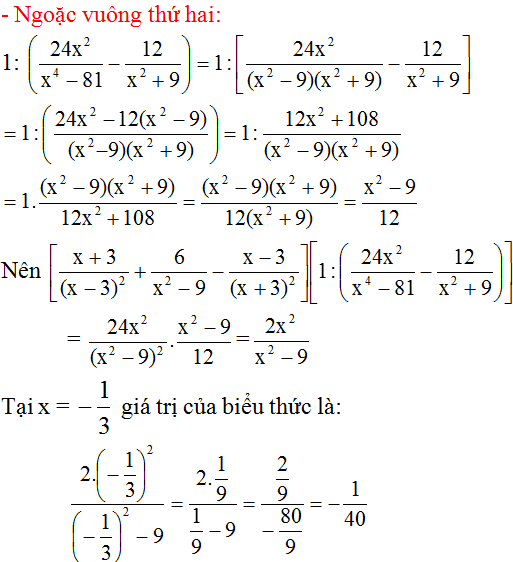




Câu 1:
a: \(A=\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{2}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
b: Để A=x/6 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-6x+6=0\)
=>x=3 hoặc x=2