Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Lấy (1)+(2)+(3) là tìm được z rồi thế z vào tìm x, y
b) Lấy (1) + (2) - (3) là tìm được y
\(a)\hept{\begin{cases}x-2y+z=12\\2x-y+3z=18\\-3x+3y+2z=-9\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-2y+z=12\\3y+z=-6\\6z=21\end{cases}}}\)
\(\text{Đáp số: }(x;y;z)=(\frac{16}{3};-\frac{19}{6};\frac{7}{2})\)
\(b)\hept{\begin{cases}x+y+z=7\\3x-2y+2z=5\\4x-y+3z=10\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x+y+z=7\\-5y-z=16\\0y+0z=-2\end{cases}}\)
\(\text{ Hệ phương trình vô nghiệm.}\)

1. Định lí Pytago
Trong một tam giác vuông, bình phương của cạnh huyền bằng tổng các bình phương của hai cạnh góc vuông.
ΔABC vuông tại A thì ta có:
AB2+AC2=BC2
a2+b2=c2

Bài 2
a) \(x^4-24x^2-25=0\) ( 1 )
Đặt \(t=x^2\) ( điều kiện \(t\ge0\) )
\(pt\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t^2-24t-25=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=676\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}t_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{24+\sqrt{676}}{2}=25\left(nhận\right)\\t_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{24-\sqrt{676}}{2}=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2=25\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm5\)
b)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=2\\9x+8y=34\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét \(2x-y=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2+y}{2}\)
Ta có \(9x+8y=34\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9\left(2+y\right)}{2}+8y=34\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{18+9y}{2}+8y=34\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{18+25y}{2}=34\)
\(\Leftrightarrow18+25y=68\)
\(\Rightarrow y=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{y+2}{2}=2\)
Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 3
a) \(x^2-5x+m-2=0\)
Thay \(m=-4\) vào phương trình
\(\Rightarrow x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=49\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{49}}{2}=6\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{49}}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b )
\(x^2-5x+m-2=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=33-4m\)
Theo định lý Viet
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}P=x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}\\S=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}P=x_1+x_2=5\\S=x_1x_2=m-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm dương phân biệt
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta>0\\P>0\\S>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}33-4m>0\\m-2>0\\5>0\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{33}{4}\\m>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2< m< \dfrac{33}{4}\)
Ta có \(2\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_2}}\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_2}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}}{\sqrt{x_1x_2}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}}{\sqrt{x_1x_2}}\right)^2=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}\right)^2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2+2\sqrt{x_1x_2}}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5+\sqrt{m-2}}{m-2}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20+4\sqrt{m-2}=9m-18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{m-2}=9m-38\)
\(\Leftrightarrow64m-128=\left(9m-38\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow64m-128=81m^2-684m+1444\)
\(\Leftrightarrow81m^2-748m+1572=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=50176\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{748+\sqrt{50176}}{162}=6\\m_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{748-\sqrt{50176}}{162}=\dfrac{262}{81}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(2< m< \dfrac{33}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left\{6;\dfrac{262}{81}\right\}\)

Câu 1.
a) ĐKXĐ: x ≥ 0, x ≠ 4.
Rút gọn:

b. x = 1/4 ∈ ĐKXĐ. Thay vào P, ta được:
Câu 2.
Gọi x, y (nghìn) lần lượt là giá của 1 quả dừa và 1 quả thanh long.
Điều kiện : 0 < x; y < 25.

Giải ra ta được : x = 20, y = 5 (thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán).
Vậy: Giá 1 quả dừa 20 nghìn.
Giá 1 quả thanh long 5 nghìn.

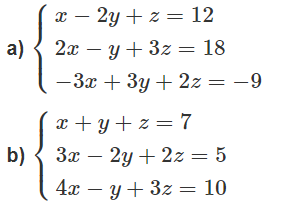 Giúp nhanh vs ạ, đng cần gấp
Giúp nhanh vs ạ, đng cần gấp

 và
và  trên hình 5 cũng có độ dài bằng nhau, nhưng liệu chúng ta có nên nói rằng chúng bằng nhau và viết
trên hình 5 cũng có độ dài bằng nhau, nhưng liệu chúng ta có nên nói rằng chúng bằng nhau và viết  thì có nhận xét gì về độ dài và hướng của chúng?
thì có nhận xét gì về độ dài và hướng của chúng?



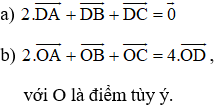
 TL:
TL:




