Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài này có vẻ lẻ quá bạn.
\(W_t=4W_đ\Rightarrow W_đ=\dfrac{W_t}{4}\)
Cơ năng: \(W=W_đ+W_t=W_t+\dfrac{W_t}{4}=\dfrac{5}{4}W_t\)
\(\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}kA^2=\dfrac{5}{4}.\dfrac{1}{2}kx^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x = \pm\dfrac{2}{\sqrt 5}A\)
M N O α α
Thời gian nhỏ nhất ứng với véc tơ quay từ M đến N.
\(\cos\alpha=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt 5}\)\(\Rightarrow \alpha =26,6^0\)
Thời gian nhỏ nhất là: \(\Delta t=\dfrac{26,6\times 2}{360}.T=\dfrac{26,6\times 2}{360}.\dfrac{2\pi}{20}=0.046s\)

Áp dụng công thức: \(A^2 = x^2 +\frac{v^2}{\omega^2} \) \(\Rightarrow A^2 = 3^2 +\frac{(60\sqrt3)^2}{\omega^2} = (3\sqrt2)^2 +\frac{(60\sqrt2)^2}{\omega^2} \)
Giải hệ trên ta được \(\omega = 20rad/s; \ A =6cm\)

Ta có: \(\begin{cases}\Delta l_1=l_1-l_0=\frac{g}{\omega^2_1}\\\Delta l_2=l_2-l_0=\frac{g}{\omega^2_2}\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\frac{\omega^2_2}{\omega^2_1}=\frac{21-l_0}{21,5-l_0}=\frac{1}{1,5}\)\(\Rightarrow l_0=20\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta l_1=0,01\left(m\right)=\frac{g}{\omega^2_1}\Rightarrow\omega_1=10\pi\left(rad/s\right)\)
KQ = 3,2 cm

\(\omega_1=\frac{2\pi}{T_1}=\frac{10\pi}{3}\); \(\omega_2=\frac{2\pi}{T_2}=\frac{10\pi}{9}\)
\(\varphi_2=\omega_2t;\omega_1t=\pi-\varphi_2\)
\(\Rightarrow t=\frac{\pi}{\omega_1+\omega_2}=0,225\left(s\right)\)

Gọi phương trình dao động là: \(x=A\cos\omega t\)
PT vận tốc là: \(v=x'=-\omega A\sin\omega t\)
Ta có: \(A\cos\omega t_0=2\)
Cần tìm:
\(v=-\omega A\sin\omega (t_0+0,5)\)
\(=-\omega A\sin(\omega .t_0+\dfrac{2\pi}{2}.0,5)\)
\(=-\omega A\sin(\omega .t_0+\dfrac{\pi}{2})\)
\(=-\dfrac{2\pi}{2} A\cos\omega t_0\)
\(=-\dfrac{2\pi}{2}.2=-2\pi(cm/s)\)
Chọn D

Khoảng thời gian giữa 2 lần liên tiếp động ăng bằng thế năng là T/4
\(\Rightarrow \dfrac{T}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{40}\)
\(\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{\pi}{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow \omega=\dfrac{2\pi}{T}=20(rad/s)\)
Biên độ dao động: \(A=\dfrac{v_{max}}{\omega}=\dfrac{100}{20}=5(cm)\)
Ban đầu, vật qua VTCB theo chiều dương trục toạ độ \(\Rightarrow \varphi=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\)
Vậy PT dao động là: \(x=5\cos(20.t-\dfrac{\pi}{2})(cm)\)

Sử sụng hệ thức: 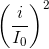 +
+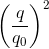 = 1
= 1
Thay số và giải hệ phương trình trìm I0 và q0
Tần số góc: ω = 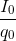 = 50 (rad/s)
= 50 (rad/s)
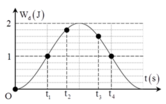
 chọn A
chọn A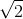
→ Biểu diễn các vị trí tương ứng trên hình tròn, ta thu được:
Đáp án C