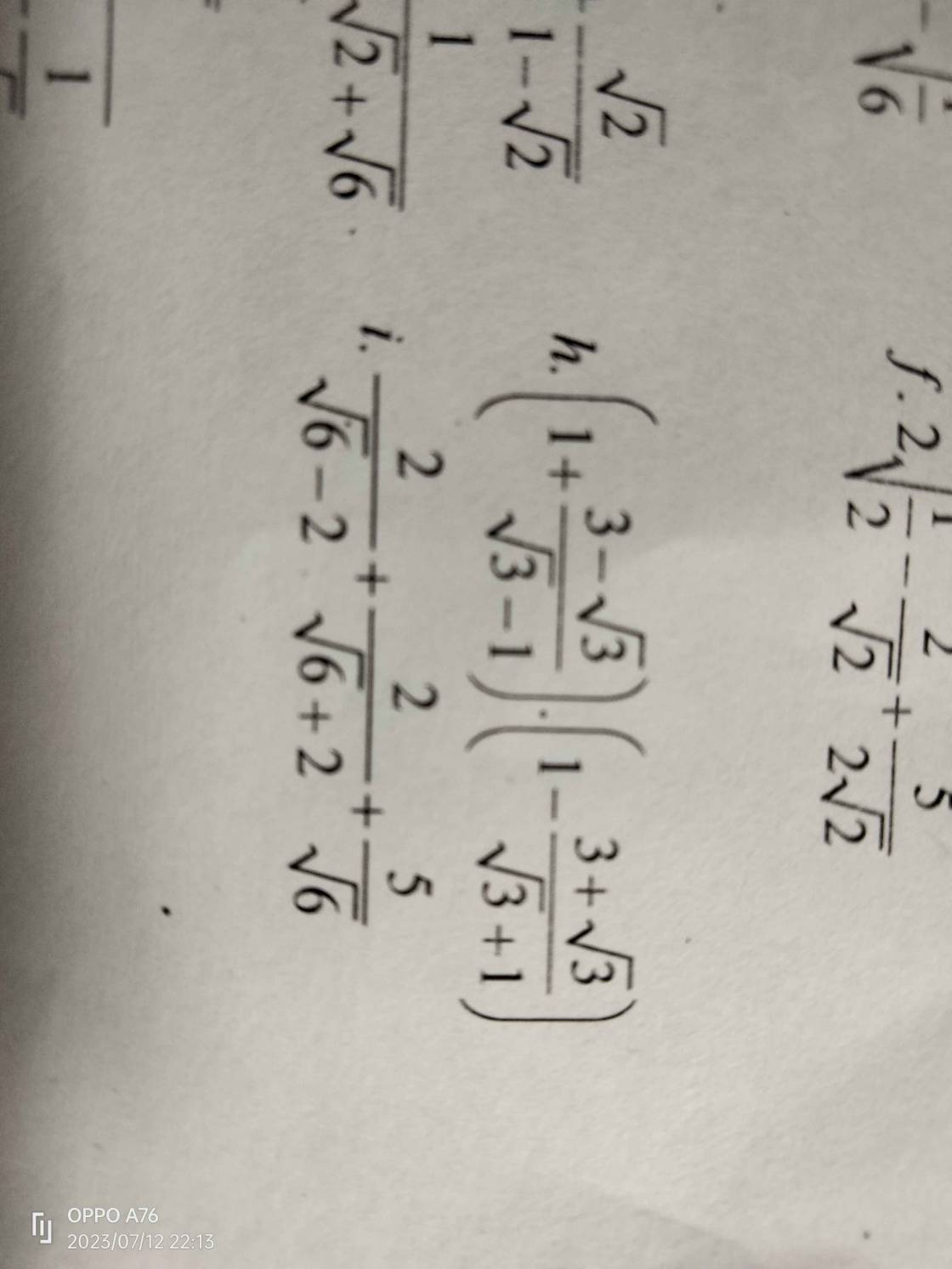Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi x là chiều cao của tam giác ; y là cạnh đáy của tam giác (x,y > 0 )
* chiều cao bằng 3/4 đáy:
x = 3/4y
=> x - 3/4y = 0 (1)
* Nếu chiều cao tăng thêm...tăng thêm 9m^2:
1/2(y-2)(x+3) = 1/2xy + 9 (sau đó bạn tự giải phương trình nha) (2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra chiều cao là 12m , cạnh đáy là 16m

cái này thì ko nhất thiết phải Cm nha bạn
Câu b kêu tìm x để B ko nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng A
Nghĩa là
\(\dfrac{4}{3-\sqrt{x}}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{3-\sqrt{x}}-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4-\left(3-\sqrt{x}\right)}{3-\sqrt{x}}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{3-\sqrt{x}}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+1>0\\3-\sqrt{x}>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+1< 0\left(VL\right)\\3-\sqrt{x}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-\sqrt{x}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 9\)
Theo Đk ta có x≥0
Vậy 0≤x<9 thì B ko nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng A
\(\sqrt{x}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+1\ge1>0\)
Hiển nhiên nhé


Để hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\dfrac{m}{3}< >-\dfrac{1}{m}\)
=>\(m^2\ne-3\)(luôn đúng)
Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}mx-y=2\\3x+my=3m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=mx-2\\3x+m\left(mx-2\right)=3m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=mx-2\\3x+m^2x-2m=3m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=mx-2\\x\left(m^2+3\right)=5m\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5m}{m^2+3}\\y=m\cdot\dfrac{5m}{m^2+3}-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5m}{m^2+3}\\y=\dfrac{5m^2-2m^2-6}{m^2+3}=\dfrac{3m^2-6}{m^2+3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x+y\right)\cdot\left(m^2+3\right)+8=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{5m+3m^2-6}{m^2+3}\cdot\left(m^2+3\right)+8=0\)
=>\(3m^2+5m-6+8=0\)
=>\(3m^2+5m+2=0\)
=>(m+1)(3m+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-1\\m=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Câu 2:
a, bạn tự vẽ được nhớ tìm tọa dộ nhé
x 0 0
y 0 0
b, Vì tung độ của điểm nằm trên P có hoành độ bằng 8
=> x = 8
Thay x = 8 vào y = 1/2x^2 ta được :
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}.64=32\)
Bài 4:
a) Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{x^2+\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}+1-\dfrac{2x+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(x\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}+1-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)+1-2\sqrt{x}-1\)
\(=x+\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}\)
\(=x-\sqrt{x}\)

Bạn nên chịu khó gõ đề ra khả năng được giúp sẽ cao hơn.
Câu h của em đây nhé
h, ( 1 + \(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\)).(1 - \(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\))
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1-3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{2}\)
= -2
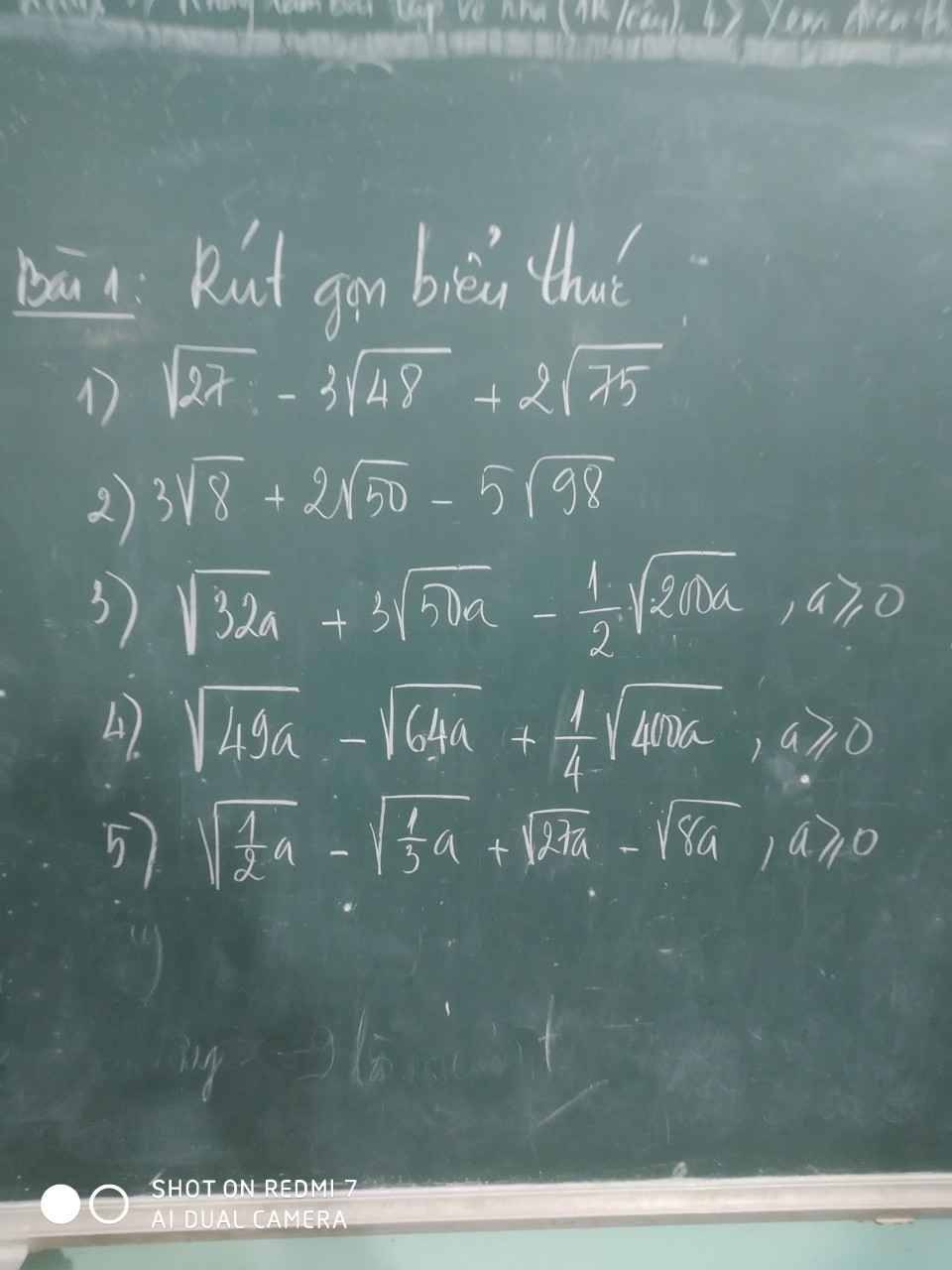
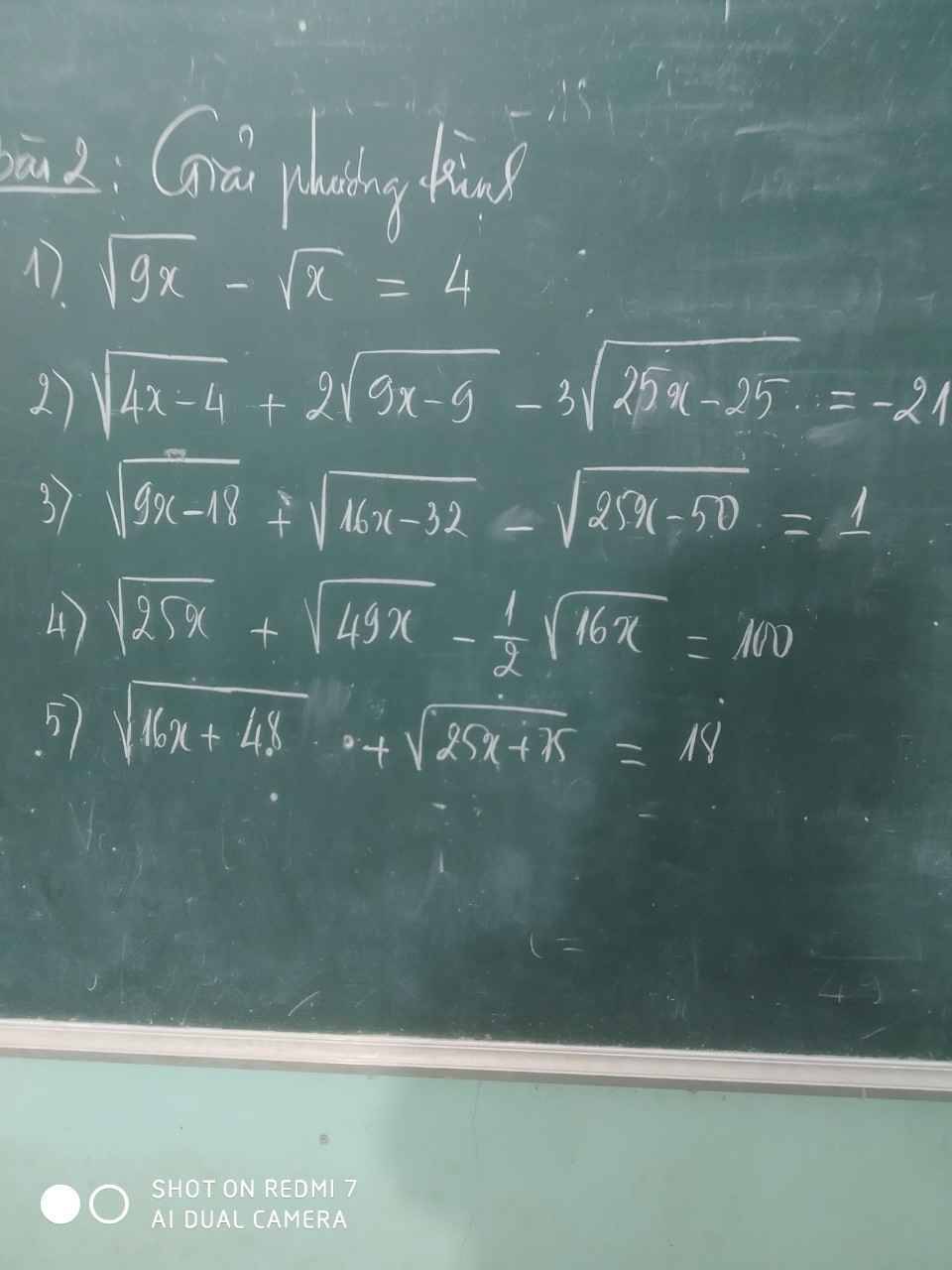

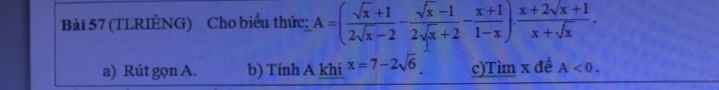

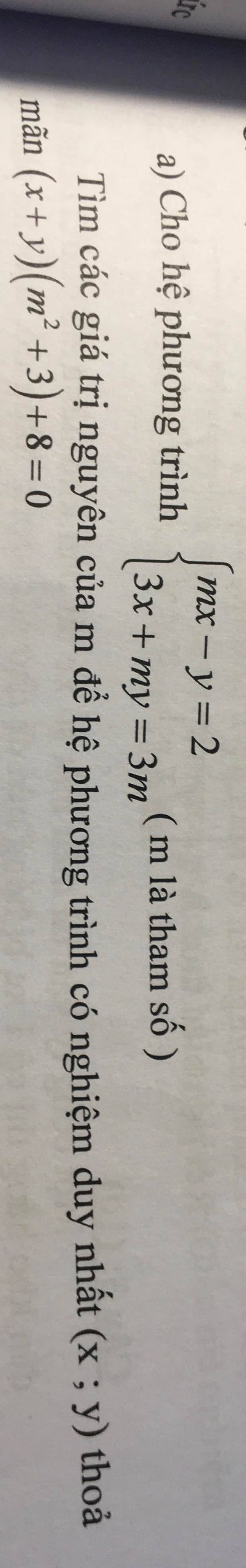
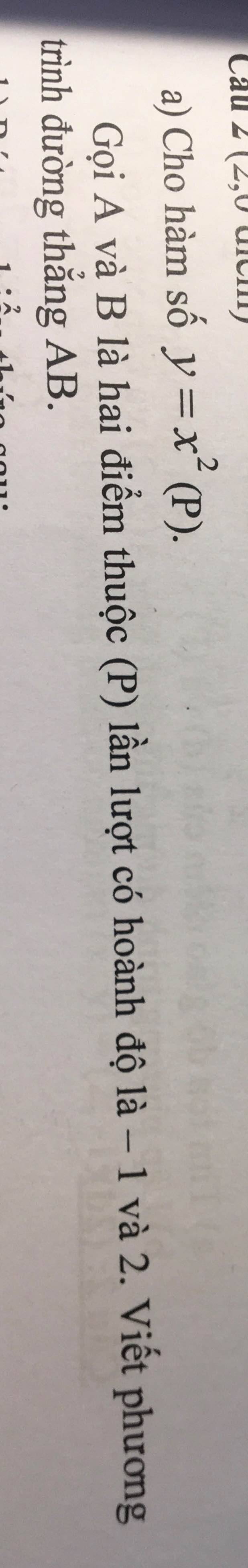
 mọi người giúp mình giải câu 2 3 4 và phần hình học vs ạ. mình cảm ơnnnnnnnnnnnnn
mọi người giúp mình giải câu 2 3 4 và phần hình học vs ạ. mình cảm ơnnnnnnnnnnnnn