
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi O là tâm đường tròn \(\Rightarrow\) O là trung điểm BC
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{ED}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow\widehat{BOE}=\widehat{EOD}=\widehat{DOC}=\dfrac{180^0}{3}=60^0\)
Mà \(OD=OE=R\Rightarrow\Delta ODE\) đều
\(\Rightarrow ED=R\)
\(BN=NM=MC=\dfrac{2R}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{NM}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow ED||BC\)
Áp dụng định lý talet:
\(\dfrac{AN}{AE}=\dfrac{MN}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{OB-BN}{BN}=\dfrac{R-\dfrac{2R}{3}}{\dfrac{2R}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) và \(\widehat{ENO}=\widehat{ANB}\) (đối đỉnh)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ENO\sim ANB\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{NBA}=\widehat{NOE}=60^0\)
Hoàn toàn tương tự, ta có \(\Delta MDO\sim\Delta MAC\Rightarrow\widehat{MCA}=\widehat{MOD}=60^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\) đều




Ta có : \(\frac{A}{B}\ge\frac{x}{4}+5\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+4\ge\frac{x}{4}+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4\sqrt{x}+16}{4}-\frac{x}{4}-\frac{20}{4}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\frac{4\sqrt{x}-x-4}{4}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-x+4\sqrt{x}-4\ge0\Leftrightarrow x-4\sqrt{x}+4\le0\)vì 4 > 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2\le0\Leftrightarrow x\le4\)
Kết hợp với đk vậy \(0\le x\le4;x\ne1\)

a, \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+y^2+3xy=5\\\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+1\right)+xy=7\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x+y\right)^2+xy=5\\\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+1\right)+xy=7\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+1\right)=-2\\\left(x+y\right)^2+xy=5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-x-y-1\right)=-2\\\left(x+y\right)^2+xy=5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=2\\4+xy=5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2-y\\4+\left(2-y\right)y=5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2-y\\2y-y^2-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2-y\\-\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2-y\\\left(y-1\right)^2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=1\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy hpt có nghiệm (x;y) = (1;1)

\(\left(d\right):\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\)\(\left(1\right)\)
Thế \(x=a,y=0\)vào phương trình \(\left(1\right)\)thỏa mãn nên \(A\left(a,0\right)\)thuộc \(\left(d\right)\).
Thế \(x=0,y=b\)vào phương trình \(\left(1\right)\)thỏa mãn nên \(B\left(0,b\right)\)thuộc \(\left(d\right)\).
Do đó ta có đpcm.

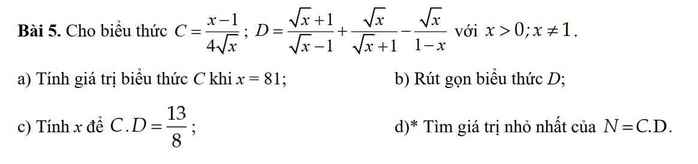


 Mọi người giúp e làm câu 4c và bài 5 ạ
Mọi người giúp e làm câu 4c và bài 5 ạ





 ai giúp mình giải câu này với ạ, mình cám ơn mn nhiều
ai giúp mình giải câu này với ạ, mình cám ơn mn nhiều
\(a,C=\dfrac{81-1}{4\cdot9}=\dfrac{80}{36}=\dfrac{20}{9}\\ b,D=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1+x-\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\\ D=\dfrac{2x+2\sqrt{x}+1}{x-1}\\ c,CD=\dfrac{x-1}{4\sqrt{x}}\cdot\dfrac{2x+2\sqrt{x}+1}{x-1}=\dfrac{2x+2\sqrt{x}+1}{4\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{13}{8}\\ \Leftrightarrow52\sqrt{x}=16x+16\sqrt{x}+8\\ \Leftrightarrow16x-36\sqrt{x}+8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-9\sqrt{x}+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=2\\\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{1}{16}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,N=CD=\dfrac{2x+2\sqrt{x}+1}{4\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4\sqrt{x}}\\ \Leftrightarrow N\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{4\sqrt{x}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=2\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{8}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{2}\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow4x=2\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(N_{min}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{2}\)