
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, Xét x=0 không phải nghiệm pt chia 2 vế cho x2 , đặt t= x+1/x từ đó suy ra phương trình ẩn t, giải ra ta được các phương trình ẩn x rồi ra x.
b, Tách đa thức thành tích của đơn thức (x+1) và 1 đa thức bậc 4 rồi làm như câu a,.
\(2x^4+3x^3-x^2+3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+4x^3-x^3-2x^2+x^2+2x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3.\left(x+2\right)-x^2.\left(x+2\right)+x.\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right).\left(2x^3-x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right).\left(2x^3+x^2-2x^2-x+2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right).\left(2x+1\right).\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\2x+1=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
\(\text{Vì }x^2-x+1=x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(S=\left\{-2,-\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)

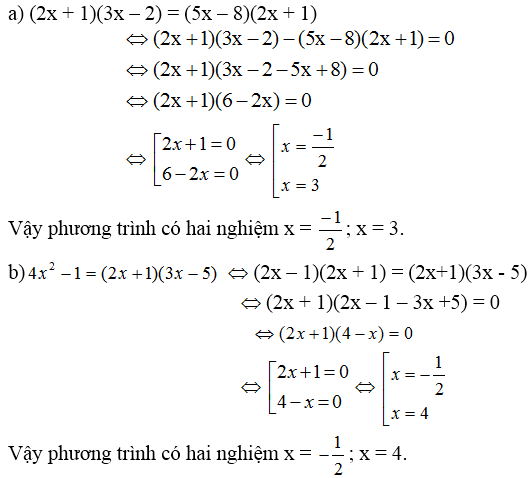
a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

a, \(1-\frac{2x-1}{9}=3-\frac{3x-3}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{108-12\cdot\left(2x-1\right)}{108}=\frac{108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)}{108}\)
\(\Rightarrow108-12\cdot\left(x-1\right)=108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow108-24x+12=324-27x+27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=231\)
\(\Rightarrow x=77\)
c,\(\frac{3}{4x-20}+\frac{15}{50-2x^2}+\frac{7}{6x+30}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+15\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+7\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow900x+4500-36x^3-180x^2+360x^2+1800x-1800x-9000+1400x-56x^3-7000+280x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-92x^3+460x^2+2300x-11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow92x^3-460x^2-2300x+11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=5\end{cases}}\)
a) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta được: 2.3 + 3 < 9 <=> 9 < 9 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình2x + 3 < 9
b) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: -4.3 > 2.3 + 5 => -12 > 11 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình -4x > 2x + 5
c) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: 5 - 3 > 3.3 -12 => 2 > -3 (khẳng định đúng)
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của bất phương trình 5 - x > 3x - 12

a,\(\frac{2x+5}{3}-2=\frac{3x-7}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(2x+5\right)-30=3\left(3x-7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x+25-30=9x-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-22\)
vậy....................
\(b,\frac{x}{6}+x=\frac{2x+1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+12x=6\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14x=12x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
vậy.....................
c,\(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{2x-1}{3}=-\frac{5x}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-4\left(2x-1\right)=-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-8x+4=-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=-4\left(PTVN\right)\)
VẬY................
P/s : bạn chú ý \(\Rightarrow\)với \(\Leftrightarrow\)nha

a) \(x^3-2x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(x^3-x^2-x^2+x-6x+6=0\)
\(x^2\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x^2-x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x^2-2x+3x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\left\{2;-3\right\}\end{cases}}\)
\(a,x^3-2x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^2\right)-\left(x^2-x\right)-\left(6x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x^2-3x\right)+\left(2x-6\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\left(h\right)x+2=0\left(h\right)x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(h\right)x=-2\left(h\right)x=3\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-2;1;3\right\}\)
P/S: (h) là hoặc nhé

a: 3x<2x+5
=>3x-2x<5
=>x<5
b: 2x+1<x+4
=>2x-x<4-1
=>x<3
c: \(-2x>-3x+3\)
=>-2x+3x>3
hay x>3
d: -4x-2>-5x+6
=>-4x+5x>6+2
=>x>8

a, Đặt pt trên là (1)
Nhận thấy : x = 0 không là nghiệm của (1)
Với x khác 0 , chia cả 2 vế của (1) cho \(x^2\) ta được :
\(2x^2+3x-1+\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{2}{x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)+3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)-1=0\circledast\)
Đặt \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=y^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x.\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}=4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}=4^2-2\)
\(\Rightarrow\circledast\Leftrightarrow2\left(y^2-2\right)+3y-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2+3y-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2-2y+5y-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2y+5\right)\left(y-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{-5}{2}\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\)+ Với \(y=\dfrac{-5}{2}\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+2}{2x}=\dfrac{-5x}{2x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+5x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+x+4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x+1\right)+2\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
+ Với \(y=1\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{x}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+1}{x}=\dfrac{x}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+1=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x.\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}=-1+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
=> Vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{-2;-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
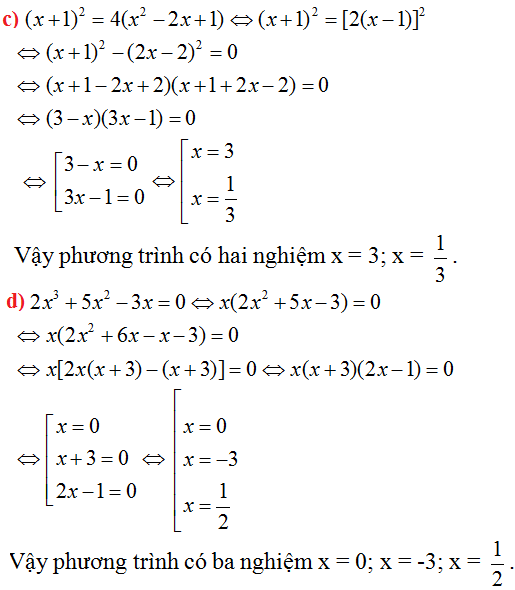

\(2x^3+5x^2-3x=0\)
\(x\left(2x^2+5x-3\right)=0\)
\(x\left(2x^2+6x-x-3\right)=0\)
\(x\left[2x\left(x+3\right)-\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(x\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
tự làm nốt
hok tốt
Ta có:
\(2x^3+5x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(2x^2+5x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(2x^2+6x-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(2x\left(x+3\right)-\left(x+3\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
=>x=0 hoặc x=3 hoặc 2x-1=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=3 hoặc x=1/2
Vậy ...