Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

câu 1
⇒ \(\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}\) - \(\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}\) -\(\dfrac{2cos4x}{2sinxcosx}\) =0
⇔ \(\dfrac{cos^2x-sin^2x}{sinx.cosx}\) -\(\dfrac{cos4x}{sinx.cosx}\)= 0
⇔ \(\dfrac{cos2x-cos4x}{sinx.cosx}\) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=cos4x\\sin2x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=4x+k2\pi\\2x=-4x+k2\pi\\2x=k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-k\pi\\x=\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) (k∈ Z)
câu 2 dùng công thức biến đổi tích thành tổng thành cos 4x + cos 2x sau đó phương trình trở thành sin x - cos 4x=0

Điều kiện 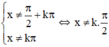
tanx – 2.cotx + 1 = 0
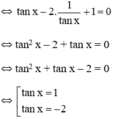
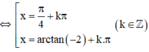 (Thỏa mãn điều kiện).
(Thỏa mãn điều kiện).
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm
{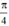 + kπ; arctan(-2) + kπ} (k ∈ Z)
+ kπ; arctan(-2) + kπ} (k ∈ Z)


ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\)
\(tanx+\dfrac{1}{tanx}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow tan^2x+1=2tanx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(tanx-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tanx=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\) (thỏa mãn)

Đối với những phương trình lượng giác chứa tanx, cotx, sin2x hoặc cos2x, ta có thể đưa về phương trình chứa cosx, sinx, sin2x, hoặc cos2x ngoài ra cũng có thể đặt ẩn phụ t = tanx để đưa về một phương trình theo t.
Cách 1: Điều kiện của phương trình:
sin2x ≠ 0 ⇔ cos2x ≠ 1 hoặc cos2x ≠ -1 (1)
Ta có:
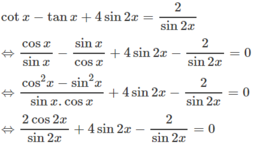
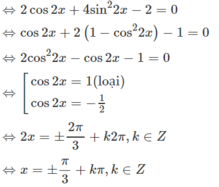
Cách 2. Đặt t = tanx
Điều kiện t ≠ 0
Phương trình đã cho có dạng
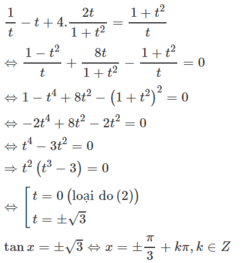

Điều kiện của phương trình: sinx ≠ 0, cos ≠ 0, tan ≠ -1.
Biến đổi tương đương đã cho, ta được
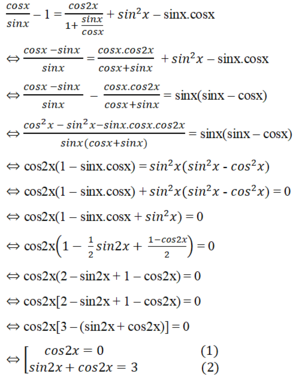
Phương trình (2) vô nghiệm vì |sin2x + cos2x| ≥ √2.
Phương trình (1) có nghiệm 2x = π/2+kπ,k ∈ Z
⇒ x = π/4+ k π/2,k ∈ Z.
Giá trị x = π/4+ k π/2, k = 2n + 1,
với n ∈ Z bị loại do điều kiện tanx ≠ -1.

cotx - cot2x = tanx + 1 (1)
Điều kiện: sinx ≠ 0 và cosx ≠ 0. Khi đó:
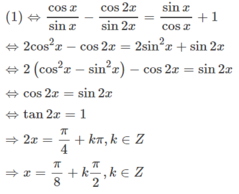

Lời giải:
ĐK:..................
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \tan x+\frac{1}{\tan x}+\frac{2}{\tan 2x}(1-2\cos x)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{\tan ^2x+1}{\tan x}+\frac{1-\tan ^2x}{\tan x}(1-2\cos x)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x+1+(1-\tan ^2x)(1-2\cos x)=2\tan x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-1)^2-(\tan x-1)(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-1)[\tan x-1-(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)]=0\)
Nếu $\tan x-1=0$ thì $x=k\pi +\frac{\pi}{4}$
Nếu $\tan x-1-(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\tan x+1)\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow (\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}+1)\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow \sin x+\cos x=1$
$\Rightarrow (\sin x+\cos x)^2=1$
$\Leftrightarrow 1+2\sin x\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow \sin x\cos x=0$ (trái điều kiện xác định)
Vậy...............
Lời giải:
ĐK:..................
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \tan x+\frac{1}{\tan x}+\frac{2}{\tan 2x}(1-2\cos x)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{\tan ^2x+1}{\tan x}+\frac{1-\tan ^2x}{\tan x}(1-2\cos x)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x+1+(1-\tan ^2x)(1-2\cos x)=2\tan x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-1)^2-(\tan x-1)(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-1)[\tan x-1-(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)]=0\)
Nếu $\tan x-1=0$ thì $x=k\pi +\frac{\pi}{4}$
Nếu $\tan x-1-(\tan x+1)(1-2\cos x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\tan x+1)\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow (\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}+1)\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow \sin x+\cos x=1$
$\Rightarrow (\sin x+\cos x)^2=1$
$\Leftrightarrow 1+2\sin x\cos x=1$
$\Leftrightarrow \sin x\cos x=0$ (trái điều kiện xác định)
Vậy...............