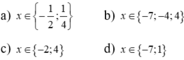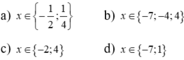
a)
3...">
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời. a) đặt \(\left(x^2+x\right)\)là \(y\) ta có: \(3y^2-7y+4\)\(=0\) <=>\(\left(3y-4\right)\left(y-1\right)=0\) còn lại bạn tự xử nhé Nhìn sơ qua thì thấy bài 3, b thay -2 vào x rồi giải bình thường tìm m Bài 2: a) \(x+x^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=0-1\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-1\end{cases}}\) b) \(0x-3=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow0x=3\) \(\Rightarrow vonghiem\) c) \(3y=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow y=0\) a/ Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{x+1}{x-2}=a\\\frac{x+1}{x-4}=b\end{cases}}\) thì có \(a^2+b-\frac{12b^2}{a^2}=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(a^2-3b\right)\left(a^2+4b\right)=0\) b/ \(2x^2+3xy-2y^2=7\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-y\right)\left(x+2y\right)=7\) chẳng ai giải, thôi mình giải vậy! a) Đặt \(y=x^2+4x+8\),phương trình có dạng: \(t^2+3x\cdot t+2x^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow t^2+xt+2xt+2x^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t+x\right)+2x\left(t+x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+t\right)\left(t+x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+4x+8+x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-4\end{cases}}\)vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là:S={-2;-4} b) nhân 2 vế của phương trình với 12 ta được: \(\left(6x+7\right)^2\left(6x+8\right)\left(6x+6\right)=72\) Đặt y=6x+7, ta được:\(y^2\left(y+1\right)\left(y-1\right)=72\) giải tiếp ra ta sẽ được S={-2/3;-5/3} c) \(\left(x-2\right)^4+\left(x-6\right)^4=82\) S={3;5} d)s={1} e) S={1;-2;-1/2} f) phương trình vô nghiệm a)\(\frac{x}{5}+\frac{2x+1}{3}=\frac{x-5}{15}\) \(\frac{3x}{15}+\frac{10x+5}{15}=\frac{x-5}{15}\) \(3x+10x+5=x-5\) \(13x+5-x+5=0\) \(12x=-10\) \(x=-\frac{5}{6}\) a) 7x - 35 = 0 <=> 7x = 0 + 35 <=> 7x = 35 <=> x = 5 b) 4x - x - 18 = 0 <=> 3x - 18 = 0 <=> 3x = 0 + 18 <=> 3x = 18 <=> x = 5 c) x - 6 = 8 - x <=> x - 6 + x = 8 <=> 2x - 6 = 8 <=> 2x = 8 + 6 <=> 2x = 14 <=> x = 7 d) 48 - 5x = 39 - 2x <=> 48 - 5x + 2x = 39 <=> 48 - 3x = 39 <=> -3x = 39 - 48 <=> -3x = -9 <=> x = 3 a) \(\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-6x+9\right)-\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2-2x-1=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow-8x+8=0\Leftrightarrow-8\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\) Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {1} b) \(\left(x^2-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)=\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x-1\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)-\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4\right)\left(2x+3-x+1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\) <=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0 hoặc x + 4 = 0 <=> x = 2 hoặc x = -2 hoặc x = -4 Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = { 2; -2; -4 } c) \(\left(3x-7\right)^2-4\left(x+1\right)^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-42x+49\right)-4\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-42x+49-4x^2-8x-4=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow5x^2-50x+45=0\Leftrightarrow5\left(x-1\right)\left(x-9\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-9=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=9\end{cases}}\) Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = { 1; 9 } a) pt <=> ( x - 1 )3 + x2( x - 1 ) = 0 <=> ( x - 1 )[ ( x - 1 )2 + x2 ] = 0 <=> x = 1 Vậy pt có nghiệm x = 1 b) x2 + x - 12 = 0 <=> x2 - 3x + 4x - 12 = 0 <=> x( x - 3 ) + 4( x - 3 ) = 0 <=> ( x - 3 )( x + 4 ) = 0 <=> x = 3 hoặc x = -4 Vậy S = { 3 ; -4 } c) x + x4 = 0 <=> x( x3 + 1 ) = 0 <=> x( x + 1 )( x2 - x + 1 ) = 0 <=> x = 0 hoặc x = -1 Vậy S = { 0 ; -1 } a,\(x^3-3x^2+3x-1+x\left(x^2-x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-3x^2+3x-1\right)+x\left(x^2-x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^3+x^2\left(x-1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+x^2\right]=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=1\) Bài 3: a) \(\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).\left(3x+9\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).3.\left(x+3\right)=0\) Vì \(3\ne0.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\2x=5\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{6;\frac{5}{2};-3\right\}.\) b) \(2x.\left(x-3\right)+5.\left(x-3\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right).\left(2x+5\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\2x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{3;-\frac{5}{2}\right\}.\) c) \(\left(x^2-4\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2^2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(3x-1\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{2;\frac{1}{3}\right\}.\) Chúc bạn học tốt!