Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.
giải các phương trình sau:
a) 6x-3= 4x+5
b) \(\dfrac{2x+3}{x+1}\)- \(\dfrac{6}{x}\)= 2
c) \(|3x-1|\)=3x

a)\(6x-3=4x+5\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-3-4x-5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=4\)
Vậy x=4
b)\(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}-\frac{6}{x}=2\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{6x+6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x-6x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-3x-6=2\left(x^2+x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-3x-6-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-5x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{6}{5}\)
Vậy \(x=-\frac{6}{5}\)
c)\(\left|3x-1\right|=3x\left(1\right)\)
TH1:\(x\ge\frac{1}{3}\).PT(1) có dạng:3x-1=3x
0x=1
PT vô nghiệm
TH2:\(x< \frac{1}{3}\).PT(1) có dạng:1-3x=3x
\(\Rightarrow6x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{6}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm là \(\frac{1}{6}\)
a, \(6x-3=4x+5 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-4x=5+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
vậy no của pt là : x = 4
b, \(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}-\frac{6}{x}=2\)
ĐKXĐ : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x-6x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2-3x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-3x-6=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-6}{5}\)
vậy no của pt là x=-6/5
c, \(\left|3x-1\right|=3x\)
Với \(3x-1\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-1=3x\Leftrightarrow-1=0\)( vô lí )

Mấy này bạn quy đồng lên cùng mẫu xong khử mẫu rồi giải. Dễ mà.

a) \(\dfrac{x}{x-3}+\dfrac{9-6x}{x^2-3x}=\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{9-6x}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-6x+9}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)^2}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x-3}{x}\)

a) 1x−3+3=x−32−x1x−3+3=x−32−x ĐKXĐ: x≠2x≠2
Khử mẫu ta được: 1+3(x−2)=−(x−3)⇔1+3x−6=−x+31+3(x−2)=−(x−3)⇔1+3x−6=−x+3
⇔3x+x=3+6−13x+x=3+6−1
⇔4x = 8
⇔x = 2.
x = 2 không thỏa ĐKXĐ.
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
b) 2x−2x2x+3=4xx+3+27

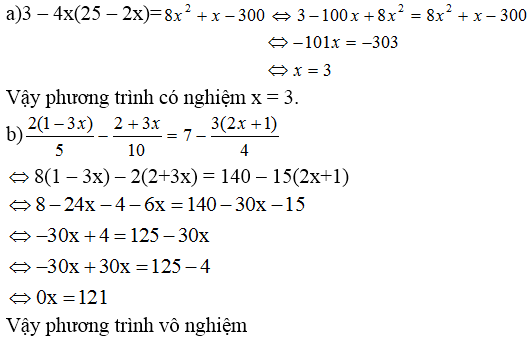


a) \(6x-3=4x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-4x=5+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
Vậy nghiệm là \(x=4\)
b) \(\dfrac{2x+3}{x+1}-\dfrac{6}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(2x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x+3\right)-6\left(x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+3x-6x-6=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x^2+3x-6x-2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy nghiệm là \(x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
c) TH1:\(3x-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=3x-1\)
Thay vào phương trình:
Được: \(3x-1=3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-3x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=1\Rightarrow\)Vô nghiệm
TH2: \(3x-1< 0\Rightarrow x< \dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=-\left(3x-1\right)=1-3x\)
Thay vào phương trình:
Được: \(1-3x=3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-3x-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{6}\)(Nhận)
Vậy nghiệm là \(x=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
a) 6x - 3 = 4x +5
<=> 6x - 4x = 5 + 3
<=> 2x = 8
<=> x = 4
Vậy tập nghiệm phương trình có S= {4}
b) \(\dfrac{2x+3}{x+1}-\dfrac{6}{x}=2\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x\left(2x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
<=> \(\dfrac{2x^2+3x-6x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
<=> \(2x^2-3x-6=2x^2+2x\)
<=>\(2x^2-2x^2-3x-2x=6\)
<=>\(-5x=6\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{-6}{5}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình S={\(\dfrac{-6}{5}\)}
c) |\(3x-1\)|=\(3x\)
+ \(3x-1>=0\) <=> x>=\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=> \(3x-1=3x\)
<=> \(0=1\) ( Vô nghiệm)
+ \(3x-1< 0\) <=> \(x< \dfrac{1}{3}\)
=> \(3x-1=-3x\)
<=> \(6x=1\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{1}{6}\) ( TM)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình S={\(\dfrac{1}{6}\)}