
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


3x3 - 3x2- 6x = 0
x ( 3x2 - 3x - 6 ) = 0
x [ 3x2 + 3x - 6x - 6 ] = 0
x [ 3x ( x + 1 ) - 6 ( x + 1 ) ] = 0
x ( 3x - 6 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc 3x - 6 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
1) x = 0
2) 3x - 6 = 0 <=> x = 2
3) x + 1 = 0 <=> x = -1
Vậy taaph nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S={0 : -1 : 2 }
\(3x^3-3x^2-6x=0\)
\(3x^3-6x^2+3x^2-6x=0\)
\(3x^2.\left(x-2\right)+3x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\left(3x^2+3x\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(3x\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=0\) \(\Rightarrow x=0\)hoặc \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=2\end{cases}}\)

a: 7x+35=0
=>7x=-35
=>x=-5
b: \(\dfrac{8-x}{x-7}-8=\dfrac{1}{x-7}\)
=>8-x-8(x-7)=1
=>8-x-8x+56=1
=>-9x+64=1
=>-9x=-63
hay x=7(loại)
a, \(7x=-35\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
b, đk : x khác 7
\(8-x-8x+56=1\Leftrightarrow-9x=-63\Leftrightarrow x=7\left(ktm\right)\)
vậy pt vô nghiệm
2, thiếu đề

`3x+7=0`
`<=>3x=-7`
`<=>x=-7/3`
Vậy `S={-7/3}`
______________________
`2x(x-2)+2x(5-3x)=0`
`<=>2x(x-2+5-3x)=0`
`<=>2x(3-2x)=0`
`@TH1:2x=0<=>x=0`
`@TH2: 3-2x=0<=>2x=3<=>x=3/2`
Vậy `S={0;3/2}`
3x+7=0
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-7\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{7}{3}\)
2x(x-2)+2x(5-3x)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2+5-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(-2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\-2x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{-3}{-2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

-3x + 18 = 0
⇔ -3x = -18
⇔ x = 6
Phương trình có tập nghiệm S = { 6 }.

3x – x + 4 = 0 ⇔ 2x + 4 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -4 ⇔ x = -2
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-2}.

a/ 4x + 20 = 0
⇔4x = -20
⇔x = -5
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-5}
b/ 2x – 3 = 3(x – 1) + x + 2
⇔ 2x-3 = 3x -3+x+2
⇔2x – 3x = -3+2+3
⇔-2x = 2
⇔x = -1
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-1}
câu tiếp theo
a/ (3x – 2)(4x + 5) = 0
3x – 2 = 0 hoặc 4x + 5 = 0
- 3x – 2 = 0 => x = 3/2
- 4x + 5 = 0 => x = – 5/4
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S= {-5/4,3/2}
b/ 2x(x – 3) – 5(x – 3) = 0
=> (x – 3)(2x -5) = 0
=> x – 3 = 0 hoặc 2x – 5 = 0
* x – 3 = 0 => x = 3
* 2x – 5 = 0 => x = 5/2
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {0, 5/2}

x4-3x2+6x+13=0
<=> x4-4x2+4+x2+6x+9=0
ta co : x2 - 2 khác x-3
=> phương trình vô nghiệm
Tk mk nha ! m.n.

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
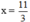
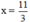
3x = 0 ⇔ x = 0. Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {0}.