Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Biến đổi :
\(4\sin x+3\cos x=A\left(\sin x+2\cos x\right)+B\left(\cos x-2\sin x\right)=\left(A-2B\right)\sin x+\left(2A+B\right)\cos x\)
Đồng nhất hệ số hai tử số, ta có :
\(\begin{cases}A-2B=4\\2A+B=3\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}A=2\\B=-1\end{cases}\)
Khi đó \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{2\left(\left(\sin x+2\cos x\right)\right)-\left(\left(\sin x-2\cos x\right)\right)}{\left(\sin x+2\cos x\right)}=2-\frac{\cos x-2\sin x}{\sin x+2\cos x}\)
Do đó,
\(F\left(x\right)=\int f\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(2-\frac{\cos x-2\sin x}{\sin x+2\cos x}\right)dx=2\int dx-\int\frac{\left(\cos x-2\sin x\right)dx}{\sin x+2\cos x}=2x-\ln\left|\sin x+2\cos x\right|+C\)

Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra 5 x + 2 y + 1 3 x y - 1 + x + 1 = 5 x y - 1 + 1 3 x + 2 y + x y - 2 y
⇔ 5 x + 2 y - 1 3 x + 2 y + x + 2 y = 5 x y - 1 - 1 3 x y - 1 + ( x y - 1 ) (1)
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 + ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f (t) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra 1 ⇔ f ( x + 2 y ) = f ( x y - 1 ) ⇔ x + 2 y = x y - 1 ⇔ x + 1 = y ( x - 2 )
y = x + 1 x - 2
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2.
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm g ' ( x ) = 1 - 3 x - 2 2 > 0 , g ' ( x ) = 0 ⇔ ( x - 2 ) 2 = 3
⇔ x = 2 + 3 ( t m ) x = 2 - 3 ( L ) . Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy m i n g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và y = 1 + 3 .

Chọn đáp án B
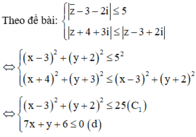
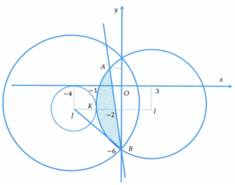
=> Tập hợp các điểm biểu diễn số phức z là miền mặt phẳng (T) mà tọa độ các điểm thỏa mãn hệ (*)
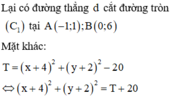


a) ĐK: \(x\ge0,x\ne1,x\ne\frac{1}{4}\)
\(A=1+\left(\frac{2x+\sqrt{x}-1}{1-x}-\frac{2x\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}+x}{1-x\sqrt{x}}\right)\frac{x-\sqrt{x}}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1+\left[\frac{\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)}-\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1+\left[\frac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{1-\sqrt{x}}-\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1-\sqrt{x}+\frac{x\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(A=\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Để \(A=\frac{6-\sqrt{6}}{5}\Rightarrow\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}=\frac{6-\sqrt{6}}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x+5=\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)x+\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)\sqrt{x}+6-\sqrt{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1-\sqrt{6}\right)x+\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{6}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-\sqrt{6}.\sqrt{x}+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=\frac{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6}}{2}\\\sqrt{x}=\frac{-\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6}}{2}\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2+\sqrt{3}\\x=2-\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\left(tmđk\right)\)
b) Xét \(A-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{3x+3-2x-2\sqrt{x}-2}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
Do \(x\ge0,x\ne1,x\ne\frac{1}{4}\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2>0\)
Lại có \(x+\sqrt{x}+1=\left(\sqrt{x}+\frac{1}{2}\right)+\frac{3}{4}>0\)
Nên \(A-\frac{2}{3}>0\Rightarrow A>\frac{2}{3}\).

Ta có 3 x + 3 - x 2 = 9 x + 9 - x + 2 = 23 + 2 = 25
Suy ra 3 x + 3 - x = 5
Do đó P = 5 + 3 x + 3 - x 1 - 3 x - 3 - x = 5 + 5 1 - 5 = - 5 2
Đáp án A

Xét tử \(\left|4-x\right|+\left|x+2\right|\ge0\)
Xét mẫu \(\left|x+5\right|+\left|x-3\right|\ge0\)
Do đó \(\frac{\left|4-x\right|+\left|x+2\right|}{\left|x+5\right|+\left|x-3\right|}\ge0\)
Nhưng đề bài cho \(\frac{\left|4-x\right|+\left|x+2\right|}{\left|x+5\right|+\left|x-3\right|}=-\frac{1}{2}<0\) nên không có giá trị nào của x thỏa mãn.
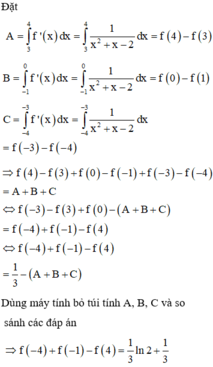

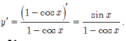
Đáp án C