Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Có: cos 2A + 2√2.cos B + 2√2.cos C = 3
⇔2cos²A - 1 + 2√2.2.cos[(B + C)/2] . cos[(B - C)/2] - 3 = 0
⇔2cos²A + 4√2.sin (A/2) . cos[(B - C)/2] - 4 = 0(1)
Ta thấy: sin(A/2) > 0 ; cos[(B - C)/2] ≤ 1
⇒VT ≤ 2cos²A + 4√2.sin(A/2) - 4
Vì tam giác ABC không tù nên 0 ≤ cos A < 1
⇒cos²A ≤ cos A
⇒VT ≤ 2cos A + 4√2.sin(A/2) - 4
⇒VT ≤ 2.[1 - 2.(sin A/2)²] + 4√2.sin(A/2) - 4
⇒VT ≤ -4.(sin A/2)² + 4√2.sin(A/2) - 2
⇒VT ≤ -2(√2.sin A/2 - 1)² ≤ 0(2)
Kết hợp (1)(2) thì đẳng thức xảy ra khi tất cả các dấu = ở trên xảy ra
⇔cos [(B - C)/2] = 1 và cos²A = cos A và √2.sin A/2 - 1 = 0
⇔góc B = góc C và cos A = 0 và sin A/2 = 1/√2
⇔ góc B = góc C và góc A = 90 độ
Vậy góc A = 90 độ, góc B = góc C = 45 độ

Câu a)
Ta sử dụng 2 công thức:
\(\bullet \tan (180-\alpha)=-\tan \alpha\)
\(\bullet \tan (\alpha+\beta)=\frac{\tan \alpha+\tan \beta}{1-\tan \alpha.\tan \beta}\)
Áp dụng vào bài toán:
\(\text{VT}=\tan A+\tan B+\tan C=\tan A+\tan B+\tan (180-A-B)\)
\(=\tan A+\tan B-\tan (A+B)=\tan A+\tan B-\frac{\tan A+\tan B}{1-\tan A.\tan B}\)
\(=(\tan A+\tan B)\left(1+\frac{1}{1-\tan A.\tan B}\right)=(\tan A+\tan B).\frac{-\tan A.\tan B}{1-\tan A.\tan B}\)
\(=-\tan A.\tan B.\frac{\tan A+\tan B}{1-\tan A.\tan B}=-\tan A.\tan B.\tan (A+B)\)
\(=\tan A.\tan B.\tan (180-A-B)\)
\(=\tan A.\tan B.\tan C=\text{VP}\)
Do đó ta có đpcm
Tam giác $ABC$ có ba góc nhọn nên \(\tan A, \tan B, \tan C>0\)
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy ta có:
\(P=\tan A+\tan B+\tan C\geq 3\sqrt[3]{\tan A.\tan B.\tan C}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\tan A+\tan B+\tan C\geq 3\sqrt[3]{\tan A+\tan B+\tan C}\)
\(\Rightarrow P\geq 3\sqrt[3]{P}\)
\(\Rightarrow P^3\geq 27P\Leftrightarrow P(P^2-27)\geq 0\)
\(\Rightarrow P^2-27\geq 0\Rightarrow P\geq 3\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy \(P_{\min}=3\sqrt{3}\). Dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(\angle A=\angle B=\angle C=60^0\)
Câu b)
Ta sử dụng 2 công thức chính:
\(\bullet \tan (\alpha+\beta)=\frac{\tan \alpha+\tan \beta}{1-\tan \alpha.\tan \beta}\)
\(\bullet \tan (90-\alpha)=\frac{1}{\tan \alpha}\)
Áp dụng vào bài toán:
\(\text{VT}=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2}.\tan \frac{C}{2}+\tan \frac{C}{2}.\tan \frac{A}{2}\)
\(=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+\tan \frac{C}{2}(\tan \frac{A}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2})\)
\(=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+\tan (90-\frac{A+B}{2})(\tan \frac{A}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2})\)
\(=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+\frac{\tan \frac{A}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2}}{\tan (\frac{A+B}{2})}\)
\(=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+\frac{\tan \frac{A}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2}}{\frac{\tan \frac{A}{2}+\tan \frac{B}{2}}{1-\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}}}\)
\(=\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}+1-\tan \frac{A}{2}.\tan \frac{B}{2}=1=\text{VP}\)
Ta có đpcm.
Cũng giống phần a, ta biết do ABC là tam giác nhọn nên
\(\tan A, \tan B, \tan C>0\)
Đặt \(\tan A=x, \tan B=y, \tan C=z\). Ta có: \(xy+yz+xz=1\)
Và \(T=x+y+z\)
\(\Rightarrow T^2=x^2+y^2+z^2+2(xy+yz+xz)\)
Theo hệ quả quen thuộc của BĐT Cauchy:
\(x^2+y^2+z^2\geq xy+yz+xz\)
\(\Rightarrow T^2\geq 3(xy+yz+xz)=3\)
\(\Rightarrow T\geq \sqrt{3}\Leftrightarrow T_{\min}=\sqrt{3}\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi \(x=y=z=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\Leftrightarrow \angle A=\angle B=\angle C=60^0\)

1.
\(sinA+sinB-sinC=2sin\dfrac{A+B}{2}.cos\dfrac{A-B}{2}-sin\left(A+B\right)\)
\(=2sin\dfrac{A+B}{2}.cos\dfrac{A-B}{2}-2sin\dfrac{A+B}{2}.cos\dfrac{A+B}{2}\)
\(=2sin\dfrac{A+B}{2}.\left(cos\dfrac{A-B}{2}-cos\dfrac{A+B}{2}\right)\)
\(=2sin\dfrac{A+B}{2}.2sin\dfrac{A}{2}.sin\dfrac{B}{2}\)
\(=4sin\dfrac{A}{2}.sin\dfrac{B}{2}.cos\dfrac{C}{2}\)
Sao t lại đc như này v, ai check hộ phát

Theo tính chất của tam giác, ta có:
\(A+B+C=180^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{A+B+C}{2}=90^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{B+C}{2}=90^0-\dfrac{A}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow tan\left(\dfrac{B+C}{2}\right)=tan\left(90^0-\dfrac{A}{2}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow tan\left(\dfrac{B+C}{2}\right)=cot\left(\dfrac{A}{2}\right)\)

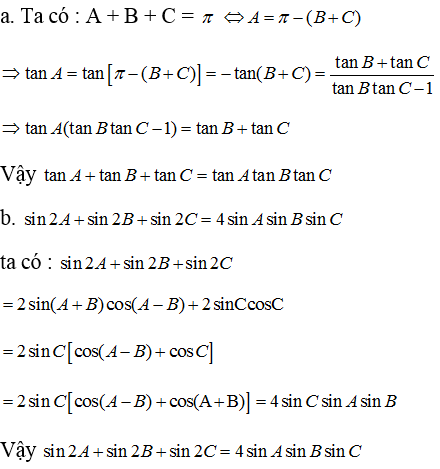
\(\dfrac{A}{2}+\dfrac{B}{2}=\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\dfrac{C}{2}\Rightarrow tan\left(\dfrac{A}{2}+\dfrac{B}{2}\right)=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\dfrac{C}{2}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{tan\dfrac{A}{2}+tan\dfrac{B}{2}}{1-tan\dfrac{A}{2}tan\dfrac{B}{2}}=cot\dfrac{C}{2}=\dfrac{1}{tan\dfrac{C}{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow tan\dfrac{A}{2}.tan\dfrac{C}{2}+tan\dfrac{B}{2}tan\dfrac{C}{2}=1-tan\dfrac{A}{2}tan\dfrac{B}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow tan\dfrac{A}{2}tan\dfrac{B}{2}+tan\dfrac{B}{2}tan\dfrac{C}{2}+tan\dfrac{C}{2}tan\dfrac{A}{2}=1\)
Ta có:
\(tan\dfrac{A}{2}+tan\dfrac{B}{2}+tan\dfrac{C}{2}\ge\sqrt{3\left(tan\dfrac{A}{2}tan\dfrac{B}{2}+tan\dfrac{B}{2}tan\dfrac{C}{2}+tan\dfrac{C}{2}tan\dfrac{A}{2}\right)}=\sqrt{3}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(A=B=C\) hay tam giác ABC đều