Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta có :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1.x_2=-\left(2m+3\right)\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(A=\left|\frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1-x_2}\right|\ge0\). A đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất \(\Leftrightarrow A^2\)đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất.
Ta có : \(A^2=\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1-x_2}\right)^2=\frac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1.x_2}=\frac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{4\left(m+1\right)^2+4\left(2m+3\right)}=\frac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{4m^2+16m+16}=\frac{\left(m+1\right)^2}{\left(m+2\right)^2}\ge0\)
Suy ra \(MinA^2=0\Leftrightarrow m=-1\)
Vậy Min A = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\)m = -1
ở bài này phải chỉ ra \(\Delta'\)lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0 , hoặc chỉ ra a và c trái dấu nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1,x2 thì mới được áp dụng hệ thức Viét

\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-2m+3=m^2+4>0\)
Phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm pb thỏa: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(B=A^2=\frac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2}{x_1^2+x_2^2-2x_1x_2}=\frac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}=\frac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)}\)
\(B=\frac{4m^2+8m+4}{4m^2+16}=\frac{m^2+2m+1}{m^2+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B\left(m^2+4\right)=m^2+2m+1\Leftrightarrow\left(B-1\right)m^2-2m+4B-1=0\) (1)
Do pt luôn có nghiệm với mọi m nên (1) luôn có nghiệm
\(\Rightarrow\Delta'=1-\left(B-1\right)\left(4B-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4B^2+5B\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le B\le\frac{5}{4}\)
Vậy \(B_{max}=\frac{5}{4}\) khi \(m=4\)

\(\Delta^`\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-\left(m^2-2\right).2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-m^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\ge m^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\ge m^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\le m\le2\)
Theo hệ thức Viet có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1.x_2=\frac{m^2-2}{2}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left|2x_1.x_2-x_1-x_2-4\right|=\left|m^2-m-6\right|=\left|\left(m-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-6,25\right|\)
Có:
\(\left(m-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le\left(-2-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=6,25\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left|\left(m-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-6,25\right|=6,25-\left(m-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le6,25\)
\(A=6,25\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
KL:..............................................

\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m-3\right)=m^2+4>0,\forall m\inℝ\)
nên phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1+x_2\).
Theo định lí Viete:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2m+2\\x_1x_2=2m-3\end{cases}}\)
\(P=\left|\frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1-x_2}\right|=\frac{\left|x_1+x_2\right|}{\left|x_1-x_2\right|}=\frac{\left|x_1+x_2\right|}{\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}}\)
\(=\frac{\left|2m+2\right|}{\sqrt{\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)}}=\frac{\left|2m+2\right|}{\sqrt{4m^2+16}}=\frac{\left|m+1\right|}{\sqrt{m^2+4}}\ge0\)
Dấu \(=\)xảy ra khi \(m=-1\).
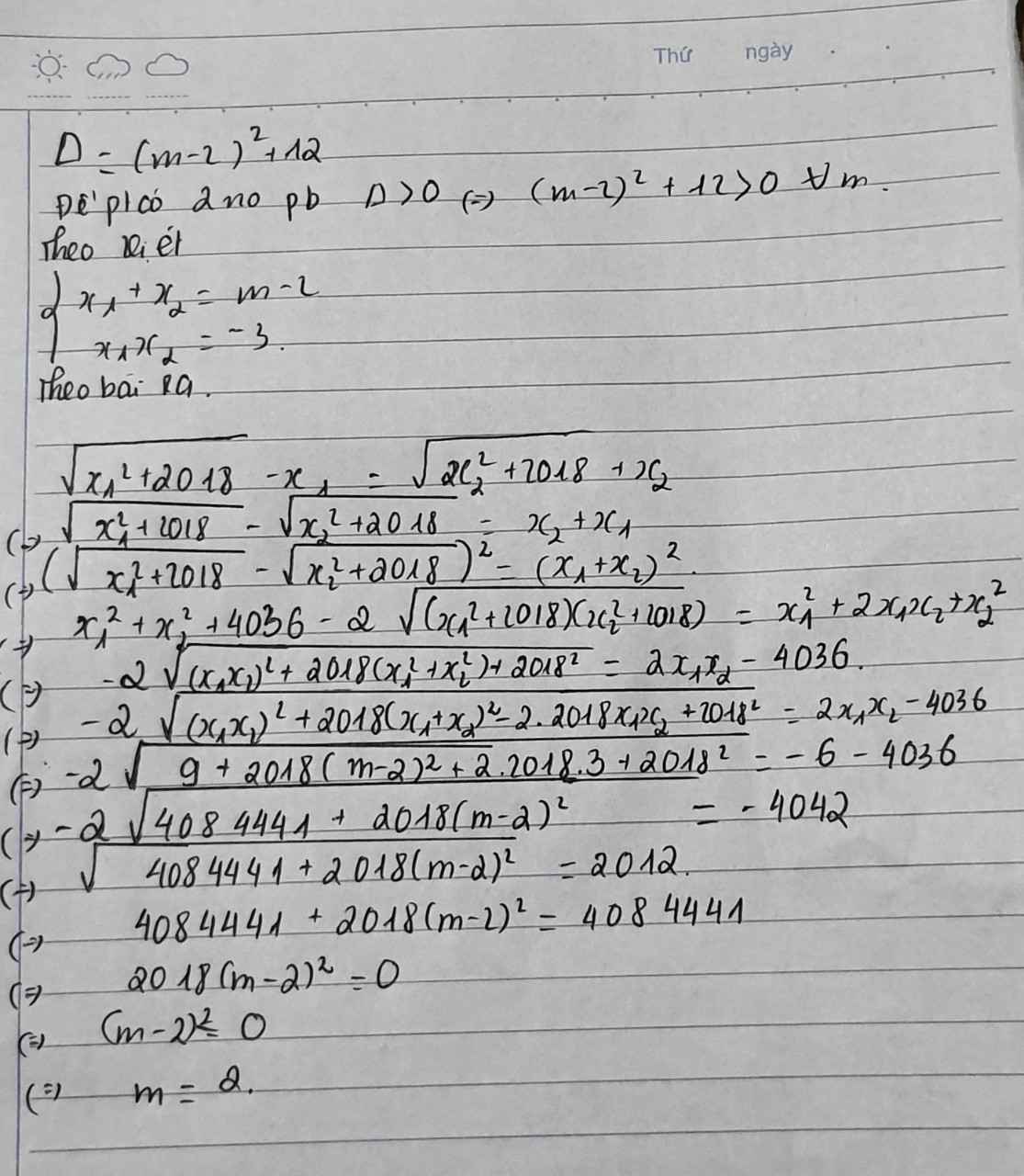
Có\(\Delta=4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)=4m^2+16>0\forall m\)
=> pt luôn có hai nghiệm pb
Theo viet có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có :\(P^2=\left(\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1-x_2}\right)^2=\dfrac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(m+1\right)^2}{4m^2+16}\)\(\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge0\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi m=-1