Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 2
\(\left|3x-101\right|=200\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-101=200\) hoặc \(3x-101=-200\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=301\) hoặc \(3x=-99\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{301}{3}\) hoặc \(x=-33\)
Bài 3:
\(\left(7x-1\right)^{12}=25^6\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(7x-1\right)^{12}=\left(5^2\right)^6\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(7x-1\right)^{12}=5^{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow7x-1=5\)
\(\Rightarrow7x=6\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{6}{7}\)

Câu 1:
Để A>1 thì \(\dfrac{x+5}{x+8}-1>0\)
=>-3/x+8>0
=>x+8<0
hay x<-8

Bài 1:
\(a)f\left(x\right)=10x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)=10.0=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(-1\right)=10\left(-1\right)=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=\frac{10}{2}=5\)
\(b)\)Vì \(f\left(x\right)=10x\)
Nên: \(f\left(a+b\right)=10\left(a+b\right)\)
Và: \(f\left(a\right)+f\left(b\right)=10a+10b=10\left(a+b\right)\)
Do đó:
\(f\left(a+b\right)=f\left(a\right)+f\left(b\right)\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(c)\)Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(x\right)=10x\\f\left(x\right)=x^2\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x^2=10x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-10x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x-10=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=10\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=10\end{cases}}\)thì \(f\left(x\right)=x^2\)

Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.
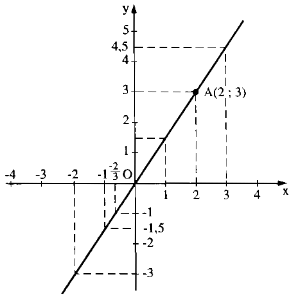
a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) =0
b)\(y=-1\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(y=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
\(y=4,5\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0
Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.

a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) = 0
b)y=−1⇒x=\(\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
b)y=0⇒x==\(\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
y=4,5⇒x=\(\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0

Bài 1 :
Vì \(\sqrt{3x+2y+z}\ge0\forall x;y;z\)
\(\left|y-\frac{1}{2}\right|\ge0\forall y\)
\(\left(z-2\right)^2\ge0\forall z\)
\(\Rightarrow A\ge2018\forall x;y;z\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+z=0\\y-\frac{1}{2}=0\\z-2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2\cdot\frac{1}{2}+2=0\\y=\frac{1}{2}\\z=2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-1\\y=\frac{1}{2}\\z=2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy........
Bài 2 :
Lý luận tương tự câu 1) ta có :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\y+1=0\\x+y+z=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=-1\\1-1+z=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=-1\\z=0\end{cases}}}\)
Thay x; y; z vào P ta có :
\(P=1^{2018}+\left(-1\right)^{2019}+0^{2020}\)
\(P=1-1+0\)
\(P=0\)