
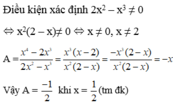
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

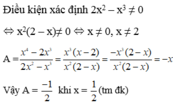

Cái biểu thức A ban ghi rõ thì mình mới giải được chứ , ghi như thế ai hiểu mà giải.

\(\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{x^2+x-6}+\frac{1}{2-x}=\frac{x+2}{x+2}+\frac{-5}{x^2+x-6}+\frac{-1}{x-2}\)
=\(\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x^2+x-6}+\frac{-5}{x^2+x-6}+\frac{-1\left(x+3\right)}{x^2+x-6}=\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-5-1\left(x+3\right)}{x^2+x-6}\)
=\(\frac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{x^2+x-6}=\frac{x^2-x-12}{x^2+x+6}\)
\(\frac{x^2-x-12}{x^2+x-6}=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
Để giá trị của PT A được xác định thì \(\left(x-2\right)\ne0\)và \(\left(x+3\right)\ne0\)
=> \(x\ne2\) và \(x\ne-3\) thì PT được xác định

Bài 1:
a: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-3+x+3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{x}=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}\)
b: Để A=3 thì 3x-9=x+1
=>2x=10
hay x=5
Bài 2:
a: \(A=\dfrac{x+x-2-2x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}:\dfrac{x+2-x}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-6}{x-2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-3}{x-2}\)
b: Để A nguyên thì \(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;1;5;-1\right\}\)

a) \(A=\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{x^2+x-6}+\frac{1}{2-x}\left(ĐK:x\ne-3;x\ne2\right)\)
\(=\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{1}{x-2}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-5-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x-4}{x-2}\)
Để \(A=-\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-4}{x-2}=-\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-4\right)=-3\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-16=-3x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=22\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{22}{7}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{22}{7}\) thì \(A=-\frac{3}{4}\)
b) \(A=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{\left(x-2\right)-2}{x-2}=1-\frac{2}{x-2}\)
Để \(A\in Z\Rightarrow\frac{2}{x-2}\in Z\Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(2\right)\)
Mà: \(Ư\left(2\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
=> \(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
+) \(x-2=1\Rightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
+) \(x-2=-1\Rightarrow x=1\left(tm\right)\)
+) \(x-2=2\Rightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
+) \(x-2=-2\Rightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1;3;4\right\}\) thì \(A\in Z\)
A=x+2/x+3-5/(x-2)(x+3)-1/x-2
A=(x+2)(x-2)-5-x-3/(x-2)(x+3)
A=x^2-4-5-x-3/(x-2)(x+3)
A=x^2-x-12/(x-2)(x+3)
A=(x+3)(x-4)/(x-2)(x+3)
A=x-4/x-2
Để A=-3/4 thì x-4/x-2=-3/4
Từ đó suy ra (x-4)4=-3(x-2)
4x-16=-3x+6
7x=22
x=22/7
b,Do A nguyên nên x-4/x-2 nguyên(x#2)
suy ra x-4-x+2 chia hết cho x-2
nên 2 chia hết cho x-2
mà ước 2=-2;-1;1;2
nên x=0;1;3;4

a, ĐKXĐ:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3\ne0\\x^2+x-6\ne0\\2-x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-3\\x^2+x-6\ne0\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-3\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(A=\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{x^2+x-6}+\dfrac{1}{2-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}\)
\(c,A=\dfrac{-3}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=\dfrac{-3}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow4\left(x-4\right)=-3\left(x-2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-16x=-3x+6\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-16x+3x-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow7x-22=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{22}{7}\)
d, \(A=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
Để \(A\in Z\Rightarrow\dfrac{2}{x-2}\in Z\Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\)
Ta có bảng:
| x-2 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 |
| x | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1;3;4\right\}\)

Bài 1 :
a) \(ĐKXĐ:x\ne1\)
\(A=\left(\frac{3}{x^2-1}+\frac{1}{x+1}\right):\frac{1}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{3+x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{x+2}{x-1}\)
b) Thay x = \(\frac{2}{5}\)vào A ta được :
\(A=\frac{\frac{2}{5}+2}{\frac{2}{5}-1}=\frac{\frac{12}{5}}{-\frac{3}{5}}=-4\)
c) Để \(A=\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{x-1}=\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+8=5x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=13\)
d) Để \(A>\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{x-1}>\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{x-1}-\frac{1}{2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4-x+1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+5>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-5\)
Bài 2 :
a) \(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(A=\frac{x^2}{x^2+x}-\frac{1-x}{x+1}\)
\(A=\frac{x}{x+1}+\frac{x-1}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{2x-1}{x+1}\)
b) Để \(A=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-1}{x+1}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
b) Để \(A< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-1}{x+1}< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-1}{x+1}-2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1-2x-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2< 0\)(luôn đúng)
Vậy A < 2 <=> mọi x

1.a)\(\frac{x^3}{x^2-4}-\frac{x}{x-2}-\frac{2}{x+2}\)
\(=\frac{x^3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{x}{x-2}-\frac{2}{x+2}\)
Để biểu thức được xác định thì:\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\ne0\)\(\Rightarrow x\ne\pm2\)
\(\left(x+2\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne-2\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne2\)
Vậy để biểu thức xác định thì : \(x\ne\pm2\)
b) để C=0 thì ....
1, c , bn Nguyễn Hữu Triết chưa lm xong
ta có : \(/x-5/=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-5=2\\x-5=-2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=7\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
thay x = 7 vào biểu thứcC
\(\Rightarrow C=\frac{4.7^2\left(2-7\right)}{\left(7-3\right)\left(2+7\right)}=\frac{-988}{36}=\frac{-247}{9}\)KL :>...
thay x = 3 vào C
\(\Rightarrow C=\frac{4.3^2\left(2-3\right)}{\left(3-3\right)\left(3+7\right)}\)
=> ko tìm đc giá trị C tại x = 3