
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x-2y=1\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}6x-4y=2\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}8x=5\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\2\cdot\frac{5}{8}+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\4y=\frac{7}{4}\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\y=\frac{7}{16}\end{cases}}\)
a) \(\hept{\begin{cases}3x-2y=1\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}6x-4y=2\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}8x=5\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\\frac{5}{4}+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\4y=\frac{7}{4}\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\y=\frac{7}{16}\end{cases}}\)
vậy hpt có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\frac{5}{8};\frac{7}{16}\right)\)
b) \(\hept{\begin{cases}4x-3y=1\\-x+2y=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}8x-6y=2\\-3x+6y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}5x=5\\-3x+6y=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\-3+6y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
vậy hpt có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;1\right)\)

(II): 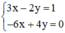
Xét: (d): 3x – 2y = 1 hay (d):
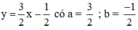
(d’): -6x + 4y = 0 hay (d’):
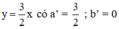
Ta có: a = a’ ; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ (II) vô nghiệm.

\(\hept{\begin{cases}2x^2+y^2-4x+2y=1\\3x^2-2y^2-6x-4y=5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2+2y+1\right)=4\\3\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-2\left(y^2+2y+1\right)=6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2=4\\3\left(x-1\right)^2-2\left(y+1\right)^2=6\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-1\right)^2=a\left(\ge0\right)\\\left(y+1\right)^2=b\left(\ge0\right)\end{cases}}\)
=> hệ phương trình \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2a+b=4\\3a-2b=6\end{cases}}\)
Tự giải tiếp nhé

Hệ phương trình tương đương \(\hept{\begin{cases}4x^2+2y^2-8x+4y=2\\3x^2-2y^2-6x-4y=5\end{cases}}\)
Cộng vế theo vế ta có phương trình:
\(7x^2-14x=7\Leftrightarrow7x^2-14x-7=0\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2+y^2-4x+2y=1\\3x^2-2y^2-6x-4y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x^2+2y^2-8x+4y=2\left(1\right)\\3x^2-2y^2-6x-4y=5\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy (1) cộng (2) ta được: \(7x^2-14x=7\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=1+\sqrt{2}\\x_2=1-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
+) T/h 1: \(x=1+\sqrt{2}\) thay vào (1) ta có:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow2\left(1+\sqrt{2}\right)^2+y^2-4\left(1+\sqrt{2}\right)+2y=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(1+2\sqrt{2}+2\right)-4\left(1+\sqrt{2}\right)+y^2+2y-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2+4\sqrt{2}+4-4-4\sqrt{2}+y^2+2y-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y^2+2y+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow y=-1\)
+) T/h 2 : \(x=1-\sqrt{2}\) thay vào (1) ta có:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow2\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)^2+y^2-4\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)+2y=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(1-2\sqrt{2}+2\right)-4\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)+y^2+2y-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2-4\sqrt{2}+4-4+4\sqrt{2}+y^2+2y-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y^2+2y+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow y=-1\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm là: \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1+\sqrt{2};-1\right);\left(1-\sqrt{2};-1\right)\)

a) (I): 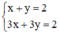
Xét (d): x + y = 2 hay (d): y = -x + 2 có a = -1; b = 2.
(d’) 3x + 3y = 2 hay (d’): y = -x + 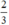 có a’ = -1 ; b’ =
có a’ = -1 ; b’ = 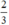
Ta có: a = a’ ; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ (I) vô nghiệm.
b) (II): 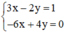
Xét: (d): 3x – 2y = 1 hay (d):
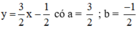
(d’): -6x + 4y = 0 hay (d’):
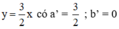
Ta có: a = a’ ; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ (II) vô nghiệm.
Kiến thức áp dụng
+ Xét hệ (I): 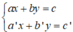
Gọi (d): ax + by = c và (d’): a’x + b’y = c’.
Số nghiệm của hệ (I) phụ thuộc vào vị trí tương đối của (d) và (d’).
(d) cắt (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có nghiệm duy nhất.
(d) // (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) vô nghiệm
(d) ≡ (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có vô số nghiệm.
+ Cho đường thẳng (d): y = ax + b và (d’): y = a’x + b’.
(d) cắt (d’) ⇔ a ≠ a’
(d) // (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b ≠ b’
(d) trùng (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b = b’.

a) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=2\\3x+3y=2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x+3y=6\\3x+3y=2\end{cases}}\)
Dễ thấy điều trên là vô lí nên hệ phương trình không có nghiệm

Từ \(\left(6x+4y-1\right)\sqrt{x+y+1}=\left(2x+2y+1\right)\sqrt{3x+21y}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+4y-1\right)^2\left(x+y+1\right)=\left(2x+2y+1\right)^2\left(3x+2y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+y-1\right)\left(12x^2+20xy+12x+8y^2+8y-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-y+1}{2}\) thay vào pt(1)
\(\frac{y^2+2y-35}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow\left(y-5\right)\left(y+7\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=5\\y=-7\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=5\Leftrightarrow x=-2\\y=-7\Leftrightarrow x=4\end{cases}}\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+2y=4\\6x+4y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+4y=8\\6x+4y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+2y=4\\\text{0=7(vô lí)}\end{matrix}\right.\) ( \(\left(6x-6x\right)+\left(4y-4y\right)=8-1\))
Vậy không có các cặp x;y thỏa mãn