
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}
a) |3x|=x+6
Với |3x|=3x ta có:
<=>3x=x+6
<=> 3x-x=6
<=> 2x=6
<=>x=3
Vậy pt có nghiệm x=3


iải phương trình gì
Đề đâu
Dora Nichow

ĐK \(a\ne\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
a. Ta có \(Q=\frac{a^3-3a^2+3a-1}{a^2-1}=\frac{\left(a-1\right)^3}{\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)}=\frac{\left(a-1\right)^2}{a+1}\)
b. Khi \(\left|x\right|=5\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=5\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Với \(x=5\Rightarrow Q=\frac{\left(5-1\right)^2}{5+1}=\frac{16}{6}=\frac{8}{3}\)
Với \(x=-5\Rightarrow Q=\frac{\left(-5-1\right)^2}{-5+1}=\frac{36}{-9}=-4\)

\(M=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)-24\)
\(M=\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]\left[\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]-24\)
\(M=\left[x\left(x+5\right)+2\left(x+5\right)\right]\left[x\left(x+4\right)+3\left(x+4\right)\right]-24\)
\(M=\left(x^2+5x+2x+10\right)\left(x^2+4x+3x+12\right)-24\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+10\right)\left(x^2+7x+12\right)-24\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+11-1\right)\left(x^2+7x+11+1\right)-24\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+11\right)^2-1-24\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+11\right)^2-25\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+11+5\right)\left(x^2+7x+11-5\right)\)
\(M=\left(x^2+7x+16\right)\left(x^2+7x+6\right)\)

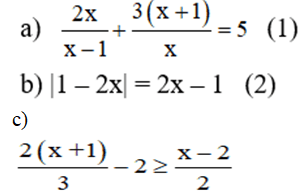
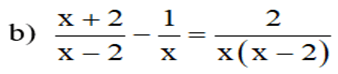








\(\dfrac{2x}{x-1}+\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{x}=5\left(\text{đ}k\text{x}\text{đ}:x\ne1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{5x\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}\\ \Rightarrow2x^2+\left(3x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)=5x^2-5x\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+3x^2-3x+3x-3=5x^2-5x\\ \Leftrightarrow5x^2-3-5x^2+5x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(b,\left|1-2x\right|=2x-1\) `(1)`
Nếu `1-2x ≥0<=> 2x≥1<=>x≥`\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) thì biểu thức `(1)` trở thành
`1-2x=2x-1`
`<=> 1+1=2x+2x`
`<=> 2=4x`
`<=> -4x=-2`
`<=>x=` \(\dfrac{-2}{-4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) ( thoả mãn đk )
Nếu `1-2x <0<=> 2x<1<=>x<`\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) thì biểu thức `(1)` trở thành
`-(1-2x)=2x-1`
`<=>-1+2x=2x-1`
`<=> 2x-2x=-1+1`
`<=>0=0` ( luôn đúng )
`c,`
\(\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3}-2\ge\dfrac{x-2}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(x+1\right)}{6}-\dfrac{2}{6}\ge\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow4x+4-2\ge3x-6\\ \Leftrightarrow4x+2\ge3x-6\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-3x\ge-6-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ge-8\)
a)\(\dfrac{2x}{x-1}+\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{x}=5\)
\(\dfrac{x\cdot2x}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}=5\)
\(\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2-x}+\dfrac{3\left(x^2-1^2\right)}{x^2-x}=5\)
\(\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2-x}+\dfrac{3x^2-3}{x^2-x}=5\)
\(\dfrac{2x^2+3x^2-3}{x^2-x}=\dfrac{5x^2-3}{x^2-x}=5\)
\(\Rightarrow5x^2-3=5\left(x^2-x\right)=5x^2-5x\)
\(\Rightarrow3=5x\)
\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
b) \(\left|1-2x\right|=2x-1\)
TH1: \(1>2x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-2x>0\\2x-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left|1-2x\right|>0\\2x-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) => Vô lí
TH2: \(1\le2x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-2x\le0\Rightarrow\left|1-2x\right|\ge0\\2x-1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|1-2x\right|=2x-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1\ge0\Rightarrow2x-1+1=2x\ge0+1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x}{2}=x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)